一、本文介绍
这次给大家带来的改进机制是 EfficientNetV1主干 ,用其替换我们YOLOv11的 特征提取网络 ,其主要思想是通过均衡地缩放网络的深度、宽度和分辨率,以提高卷积 神经网络 的性能。这种方法采用了一个简单但有效的复合系数,统一调整所有维度。经过我的实验该主干网络确实能够涨点在大中小三种物体检测上, 同时该主干网络提供多种版本 ,大家可以在 源代码 中进行修改版本的使用。 本文通过介绍其主要框架原理,然后教大家如何添加该网络结构到网络模型中。
(本文内容可根据yolov11的N、S、M、L、X进行二次缩放,轻量化更上一层)。

二、EfficientNetV1的框架原理

官方论文地址: 官方论文地址点击即可跳转
官方代码地址: 官方代码地址点击即可跳转

EfficientNetV1的主要思想是通过均衡地缩放网络的深度、宽度和 分辨率 ,以提高卷积神经网络的性能。这种方法采用了一个简单但有效的复合系数,统一调整所有维度。EfficientNet在多个方面优于现有的ConvNets,特别是在ImageNet数据集上,EfficientNet-B7模型在保持较小的大小和更快的推理速度的同时,达到了84.3%的顶级准确率。此外,EfficientNet还在CIFAR-100和Flowers等其他数据集上展示了出色的 迁移学习 性能,参数数量大大减少。
总结: EfficientNetV1的主要创新为 提出了一种新的模型缩放方法,该方法使用一个复合系数来统一地缩放网络的深度、宽度和分辨率,实现更均衡的网络扩展

这张图展示了EfficientNet提出的模型缩放方法。图中(a)表示基线网络,而图(b)-(d)表示传统的缩放方法,只增加网络的一个维度:宽度、深度或分辨率。图(e)展示了EfficientNet的创新之处,即复合缩放方法,它使用固定比例同时均匀地缩放网络的所有三个维度。
三、EfficientNetV1的核心代码
- import re
- import math
- import collections
- from functools import partial
- import torch
- from torch import nn
- from torch.nn import functional as F
- from torch.utils import model_zoo
- # Parameters for the entire model (stem, all blocks, and head)
- GlobalParams = collections.namedtuple('GlobalParams', [
- 'width_coefficient', 'depth_coefficient', 'image_size', 'dropout_rate',
- 'num_classes', 'batch_norm_momentum', 'batch_norm_epsilon',
- 'drop_connect_rate', 'depth_divisor', 'min_depth', 'include_top'])
- # Parameters for an individual model block
- BlockArgs = collections.namedtuple('BlockArgs', [
- 'num_repeat', 'kernel_size', 'stride', 'expand_ratio',
- 'input_filters', 'output_filters', 'se_ratio', 'id_skip'])
- # Set GlobalParams and BlockArgs's defaults
- GlobalParams.__new__.__defaults__ = (None,) * len(GlobalParams._fields)
- BlockArgs.__new__.__defaults__ = (None,) * len(BlockArgs._fields)
- # Swish activation function
- if hasattr(nn, 'SiLU'):
- Swish = nn.SiLU
- else:
- # For compatibility with old PyTorch versions
- class Swish(nn.Module):
- def forward(self, x):
- return x * torch.sigmoid(x)
- # A memory-efficient implementation of Swish function
- class SwishImplementation(torch.autograd.Function):
- @staticmethod
- def forward(ctx, i):
- result = i * torch.sigmoid(i)
- ctx.save_for_backward(i)
- return result
- @staticmethod
- def backward(ctx, grad_output):
- i = ctx.saved_tensors[0]
- sigmoid_i = torch.sigmoid(i)
- return grad_output * (sigmoid_i * (1 + i * (1 - sigmoid_i)))
- class MemoryEfficientSwish(nn.Module):
- def forward(self, x):
- return SwishImplementation.apply(x)
- def round_filters(filters, global_params):
- """Calculate and round number of filters based on width multiplier.
- Use width_coefficient, depth_divisor and min_depth of global_params.
- Args:
- filters (int): Filters number to be calculated.
- global_params (namedtuple): Global params of the model.
- Returns:
- new_filters: New filters number after calculating.
- """
- multiplier = global_params.width_coefficient
- if not multiplier:
- return filters
- # TODO: modify the params names.
- # maybe the names (width_divisor,min_width)
- # are more suitable than (depth_divisor,min_depth).
- divisor = global_params.depth_divisor
- min_depth = global_params.min_depth
- filters *= multiplier
- min_depth = min_depth or divisor # pay attention to this line when using min_depth
- # follow the formula transferred from official TensorFlow implementation
- new_filters = max(min_depth, int(filters + divisor / 2) // divisor * divisor)
- if new_filters < 0.9 * filters: # prevent rounding by more than 10%
- new_filters += divisor
- return int(new_filters)
- def round_repeats(repeats, global_params):
- """Calculate module's repeat number of a block based on depth multiplier.
- Use depth_coefficient of global_params.
- Args:
- repeats (int): num_repeat to be calculated.
- global_params (namedtuple): Global params of the model.
- Returns:
- new repeat: New repeat number after calculating.
- """
- multiplier = global_params.depth_coefficient
- if not multiplier:
- return repeats
- # follow the formula transferred from official TensorFlow implementation
- return int(math.ceil(multiplier * repeats))
- def drop_connect(inputs, p, training):
- """Drop connect.
- Args:
- input (tensor: BCWH): Input of this structure.
- p (float: 0.0~1.0): Probability of drop connection.
- training (bool): The running mode.
- Returns:
- output: Output after drop connection.
- """
- assert 0 <= p <= 1, 'p must be in range of [0,1]'
- if not training:
- return inputs
- batch_size = inputs.shape[0]
- keep_prob = 1 - p
- # generate binary_tensor mask according to probability (p for 0, 1-p for 1)
- random_tensor = keep_prob
- random_tensor += torch.rand([batch_size, 1, 1, 1], dtype=inputs.dtype, device=inputs.device)
- binary_tensor = torch.floor(random_tensor)
- output = inputs / keep_prob * binary_tensor
- return output
- def get_width_and_height_from_size(x):
- """Obtain height and width from x.
- Args:
- x (int, tuple or list): Data size.
- Returns:
- size: A tuple or list (H,W).
- """
- if isinstance(x, int):
- return x, x
- if isinstance(x, list) or isinstance(x, tuple):
- return x
- else:
- raise TypeError()
- def calculate_output_image_size(input_image_size, stride):
- """Calculates the output image size when using Conv2dSamePadding with a stride.
- Necessary for static padding. Thanks to mannatsingh for pointing this out.
- Args:
- input_image_size (int, tuple or list): Size of input image.
- stride (int, tuple or list): Conv2d operation's stride.
- Returns:
- output_image_size: A list [H,W].
- """
- if input_image_size is None:
- return None
- image_height, image_width = get_width_and_height_from_size(input_image_size)
- stride = stride if isinstance(stride, int) else stride[0]
- image_height = int(math.ceil(image_height / stride))
- image_width = int(math.ceil(image_width / stride))
- return [image_height, image_width]
- # Note:
- # The following 'SamePadding' functions make output size equal ceil(input size/stride).
- # Only when stride equals 1, can the output size be the same as input size.
- # Don't be confused by their function names ! ! !
- def get_same_padding_conv2d(image_size=None):
- """Chooses static padding if you have specified an image size, and dynamic padding otherwise.
- Static padding is necessary for ONNX exporting of models.
- Args:
- image_size (int or tuple): Size of the image.
- Returns:
- Conv2dDynamicSamePadding or Conv2dStaticSamePadding.
- """
- if image_size is None:
- return Conv2dDynamicSamePadding
- else:
- return partial(Conv2dStaticSamePadding, image_size=image_size)
- class Conv2dDynamicSamePadding(nn.Conv2d):
- """2D Convolutions like TensorFlow, for a dynamic image size.
- The padding is operated in forward function by calculating dynamically.
- """
- # Tips for 'SAME' mode padding.
- # Given the following:
- # i: width or height
- # s: stride
- # k: kernel size
- # d: dilation
- # p: padding
- # Output after Conv2d:
- # o = floor((i+p-((k-1)*d+1))/s+1)
- # If o equals i, i = floor((i+p-((k-1)*d+1))/s+1),
- # => p = (i-1)*s+((k-1)*d+1)-i
- def __init__(self, in_channels, out_channels, kernel_size, stride=1, dilation=1, groups=1, bias=True):
- super().__init__(in_channels, out_channels, kernel_size, stride, 0, dilation, groups, bias)
- self.stride = self.stride if len(self.stride) == 2 else [self.stride[0]] * 2
- def forward(self, x):
- ih, iw = x.size()[-2:]
- kh, kw = self.weight.size()[-2:]
- sh, sw = self.stride
- oh, ow = math.ceil(ih / sh), math.ceil(iw / sw) # change the output size according to stride ! ! !
- pad_h = max((oh - 1) * self.stride[0] + (kh - 1) * self.dilation[0] + 1 - ih, 0)
- pad_w = max((ow - 1) * self.stride[1] + (kw - 1) * self.dilation[1] + 1 - iw, 0)
- if pad_h > 0 or pad_w > 0:
- x = F.pad(x, [pad_w // 2, pad_w - pad_w // 2, pad_h // 2, pad_h - pad_h // 2])
- return F.conv2d(x, self.weight, self.bias, self.stride, self.padding, self.dilation, self.groups)
- class Conv2dStaticSamePadding(nn.Conv2d):
- """2D Convolutions like TensorFlow's 'SAME' mode, with the given input image size.
- The padding mudule is calculated in construction function, then used in forward.
- """
- # With the same calculation as Conv2dDynamicSamePadding
- def __init__(self, in_channels, out_channels, kernel_size, stride=1, image_size=None, **kwargs):
- super().__init__(in_channels, out_channels, kernel_size, stride, **kwargs)
- self.stride = self.stride if len(self.stride) == 2 else [self.stride[0]] * 2
- # Calculate padding based on image size and save it
- assert image_size is not None
- ih, iw = (image_size, image_size) if isinstance(image_size, int) else image_size
- kh, kw = self.weight.size()[-2:]
- sh, sw = self.stride
- oh, ow = math.ceil(ih / sh), math.ceil(iw / sw)
- pad_h = max((oh - 1) * self.stride[0] + (kh - 1) * self.dilation[0] + 1 - ih, 0)
- pad_w = max((ow - 1) * self.stride[1] + (kw - 1) * self.dilation[1] + 1 - iw, 0)
- if pad_h > 0 or pad_w > 0:
- self.static_padding = nn.ZeroPad2d((pad_w // 2, pad_w - pad_w // 2,
- pad_h // 2, pad_h - pad_h // 2))
- else:
- self.static_padding = nn.Identity()
- def forward(self, x):
- x = self.static_padding(x)
- x = F.conv2d(x, self.weight, self.bias, self.stride, self.padding, self.dilation, self.groups)
- return x
- def get_same_padding_maxPool2d(image_size=None):
- """Chooses static padding if you have specified an image size, and dynamic padding otherwise.
- Static padding is necessary for ONNX exporting of models.
- Args:
- image_size (int or tuple): Size of the image.
- Returns:
- MaxPool2dDynamicSamePadding or MaxPool2dStaticSamePadding.
- """
- if image_size is None:
- return MaxPool2dDynamicSamePadding
- else:
- return partial(MaxPool2dStaticSamePadding, image_size=image_size)
- class MaxPool2dDynamicSamePadding(nn.MaxPool2d):
- """2D MaxPooling like TensorFlow's 'SAME' mode, with a dynamic image size.
- The padding is operated in forward function by calculating dynamically.
- """
- def __init__(self, kernel_size, stride, padding=0, dilation=1, return_indices=False, ceil_mode=False):
- super().__init__(kernel_size, stride, padding, dilation, return_indices, ceil_mode)
- self.stride = [self.stride] * 2 if isinstance(self.stride, int) else self.stride
- self.kernel_size = [self.kernel_size] * 2 if isinstance(self.kernel_size, int) else self.kernel_size
- self.dilation = [self.dilation] * 2 if isinstance(self.dilation, int) else self.dilation
- def forward(self, x):
- ih, iw = x.size()[-2:]
- kh, kw = self.kernel_size
- sh, sw = self.stride
- oh, ow = math.ceil(ih / sh), math.ceil(iw / sw)
- pad_h = max((oh - 1) * self.stride[0] + (kh - 1) * self.dilation[0] + 1 - ih, 0)
- pad_w = max((ow - 1) * self.stride[1] + (kw - 1) * self.dilation[1] + 1 - iw, 0)
- if pad_h > 0 or pad_w > 0:
- x = F.pad(x, [pad_w // 2, pad_w - pad_w // 2, pad_h // 2, pad_h - pad_h // 2])
- return F.max_pool2d(x, self.kernel_size, self.stride, self.padding,
- self.dilation, self.ceil_mode, self.return_indices)
- class MaxPool2dStaticSamePadding(nn.MaxPool2d):
- """2D MaxPooling like TensorFlow's 'SAME' mode, with the given input image size.
- The padding mudule is calculated in construction function, then used in forward.
- """
- def __init__(self, kernel_size, stride, image_size=None, **kwargs):
- super().__init__(kernel_size, stride, **kwargs)
- self.stride = [self.stride] * 2 if isinstance(self.stride, int) else self.stride
- self.kernel_size = [self.kernel_size] * 2 if isinstance(self.kernel_size, int) else self.kernel_size
- self.dilation = [self.dilation] * 2 if isinstance(self.dilation, int) else self.dilation
- # Calculate padding based on image size and save it
- assert image_size is not None
- ih, iw = (image_size, image_size) if isinstance(image_size, int) else image_size
- kh, kw = self.kernel_size
- sh, sw = self.stride
- oh, ow = math.ceil(ih / sh), math.ceil(iw / sw)
- pad_h = max((oh - 1) * self.stride[0] + (kh - 1) * self.dilation[0] + 1 - ih, 0)
- pad_w = max((ow - 1) * self.stride[1] + (kw - 1) * self.dilation[1] + 1 - iw, 0)
- if pad_h > 0 or pad_w > 0:
- self.static_padding = nn.ZeroPad2d((pad_w // 2, pad_w - pad_w // 2, pad_h // 2, pad_h - pad_h // 2))
- else:
- self.static_padding = nn.Identity()
- def forward(self, x):
- x = self.static_padding(x)
- x = F.max_pool2d(x, self.kernel_size, self.stride, self.padding,
- self.dilation, self.ceil_mode, self.return_indices)
- return x
- ################################################################################
- # Helper functions for loading model params
- ################################################################################
- # BlockDecoder: A Class for encoding and decoding BlockArgs
- # efficientnet_params: A function to query compound coefficient
- # get_model_params and efficientnet:
- # Functions to get BlockArgs and GlobalParams for efficientnet
- # url_map and url_map_advprop: Dicts of url_map for pretrained weights
- # load_pretrained_weights: A function to load pretrained weights
- class BlockDecoder(object):
- """Block Decoder for readability,
- straight from the official TensorFlow repository.
- """
- @staticmethod
- def _decode_block_string(block_string):
- """Get a block through a string notation of arguments.
- Args:
- block_string (str): A string notation of arguments.
- Examples: 'r1_k3_s11_e1_i32_o16_se0.25_noskip'.
- Returns:
- BlockArgs: The namedtuple defined at the top of this file.
- """
- assert isinstance(block_string, str)
- ops = block_string.split('_')
- options = {}
- for op in ops:
- splits = re.split(r'(\d.*)', op)
- if len(splits) >= 2:
- key, value = splits[:2]
- options[key] = value
- # Check stride
- assert (('s' in options and len(options['s']) == 1) or
- (len(options['s']) == 2 and options['s'][0] == options['s'][1]))
- return BlockArgs(
- num_repeat=int(options['r']),
- kernel_size=int(options['k']),
- stride=[int(options['s'][0])],
- expand_ratio=int(options['e']),
- input_filters=int(options['i']),
- output_filters=int(options['o']),
- se_ratio=float(options['se']) if 'se' in options else None,
- id_skip=('noskip' not in block_string))
- @staticmethod
- def _encode_block_string(block):
- """Encode a block to a string.
- Args:
- block (namedtuple): A BlockArgs type argument.
- Returns:
- block_string: A String form of BlockArgs.
- """
- args = [
- 'r%d' % block.num_repeat,
- 'k%d' % block.kernel_size,
- 's%d%d' % (block.strides[0], block.strides[1]),
- 'e%s' % block.expand_ratio,
- 'i%d' % block.input_filters,
- 'o%d' % block.output_filters
- ]
- if 0 < block.se_ratio <= 1:
- args.append('se%s' % block.se_ratio)
- if block.id_skip is False:
- args.append('noskip')
- return '_'.join(args)
- @staticmethod
- def decode(string_list):
- """Decode a list of string notations to specify blocks inside the network.
- Args:
- string_list (list[str]): A list of strings, each string is a notation of block.
- Returns:
- blocks_args: A list of BlockArgs namedtuples of block args.
- """
- assert isinstance(string_list, list)
- blocks_args = []
- for block_string in string_list:
- blocks_args.append(BlockDecoder._decode_block_string(block_string))
- return blocks_args
- @staticmethod
- def encode(blocks_args):
- """Encode a list of BlockArgs to a list of strings.
- Args:
- blocks_args (list[namedtuples]): A list of BlockArgs namedtuples of block args.
- Returns:
- block_strings: A list of strings, each string is a notation of block.
- """
- block_strings = []
- for block in blocks_args:
- block_strings.append(BlockDecoder._encode_block_string(block))
- return block_strings
- def efficientnet_params(model_name):
- """Map EfficientNet model name to parameter coefficients.
- Args:
- model_name (str): Model name to be queried.
- Returns:
- params_dict[model_name]: A (width,depth,res,dropout) tuple.
- """
- params_dict = {
- # Coefficients: width,depth,res,dropout
- 'efficientnet-b0': (1.0, 1.0, 224, 0.2),
- 'efficientnet-b1': (1.0, 1.1, 240, 0.2),
- 'efficientnet-b2': (1.1, 1.2, 260, 0.3),
- 'efficientnet-b3': (1.2, 1.4, 300, 0.3),
- 'efficientnet-b4': (1.4, 1.8, 380, 0.4),
- 'efficientnet-b5': (1.6, 2.2, 456, 0.4),
- 'efficientnet-b6': (1.8, 2.6, 528, 0.5),
- 'efficientnet-b7': (2.0, 3.1, 600, 0.5),
- 'efficientnet-b8': (2.2, 3.6, 672, 0.5),
- 'efficientnet-l2': (4.3, 5.3, 800, 0.5),
- }
- return params_dict[model_name]
- def efficientnet(width_coefficient=None, depth_coefficient=None, image_size=None,
- dropout_rate=0.2, drop_connect_rate=0.2, num_classes=1000, include_top=True):
- """Create BlockArgs and GlobalParams for efficientnet model.
- Args:
- width_coefficient (float)
- depth_coefficient (float)
- image_size (int)
- dropout_rate (float)
- drop_connect_rate (float)
- num_classes (int)
- Meaning as the name suggests.
- Returns:
- blocks_args, global_params.
- """
- # Blocks args for the whole model(efficientnet-b0 by default)
- # It will be modified in the construction of EfficientNet Class according to model
- blocks_args = [
- 'r1_k3_s11_e1_i32_o16_se0.25',
- 'r2_k3_s22_e6_i16_o24_se0.25',
- 'r2_k5_s22_e6_i24_o40_se0.25',
- 'r3_k3_s22_e6_i40_o80_se0.25',
- 'r3_k5_s11_e6_i80_o112_se0.25',
- 'r4_k5_s22_e6_i112_o192_se0.25',
- 'r1_k3_s11_e6_i192_o320_se0.25',
- ]
- blocks_args = BlockDecoder.decode(blocks_args)
- global_params = GlobalParams(
- width_coefficient=width_coefficient,
- depth_coefficient=depth_coefficient,
- image_size=image_size,
- dropout_rate=dropout_rate,
- num_classes=num_classes,
- batch_norm_momentum=0.99,
- batch_norm_epsilon=1e-3,
- drop_connect_rate=drop_connect_rate,
- depth_divisor=8,
- min_depth=None,
- include_top=include_top,
- )
- return blocks_args, global_params
- def get_model_params(model_name, override_params):
- """Get the block args and global params for a given model name.
- Args:
- model_name (str): Model's name.
- override_params (dict): A dict to modify global_params.
- Returns:
- blocks_args, global_params
- """
- if model_name.startswith('efficientnet'):
- w, d, s, p = efficientnet_params(model_name)
- # note: all models have drop connect rate = 0.2
- blocks_args, global_params = efficientnet(
- width_coefficient=w, depth_coefficient=d, dropout_rate=p, image_size=s)
- else:
- raise NotImplementedError('model name is not pre-defined: {}'.format(model_name))
- if override_params:
- # ValueError will be raised here if override_params has fields not included in global_params.
- global_params = global_params._replace(**override_params)
- return blocks_args, global_params
- # train with Standard methods
- # check more details in paper(EfficientNet: Rethinking Model Scaling for Convolutional Neural Networks)
- url_map = {
- 'efficientnet-b0': 'https://github.com/lukemelas/EfficientNet-PyTorch/releases/download/1.0/efficientnet-b0-355c32eb.pth',
- 'efficientnet-b1': 'https://github.com/lukemelas/EfficientNet-PyTorch/releases/download/1.0/efficientnet-b1-f1951068.pth',
- 'efficientnet-b2': 'https://github.com/lukemelas/EfficientNet-PyTorch/releases/download/1.0/efficientnet-b2-8bb594d6.pth',
- 'efficientnet-b3': 'https://github.com/lukemelas/EfficientNet-PyTorch/releases/download/1.0/efficientnet-b3-5fb5a3c3.pth',
- 'efficientnet-b4': 'https://github.com/lukemelas/EfficientNet-PyTorch/releases/download/1.0/efficientnet-b4-6ed6700e.pth',
- 'efficientnet-b5': 'https://github.com/lukemelas/EfficientNet-PyTorch/releases/download/1.0/efficientnet-b5-b6417697.pth',
- 'efficientnet-b6': 'https://github.com/lukemelas/EfficientNet-PyTorch/releases/download/1.0/efficientnet-b6-c76e70fd.pth',
- 'efficientnet-b7': 'https://github.com/lukemelas/EfficientNet-PyTorch/releases/download/1.0/efficientnet-b7-dcc49843.pth',
- }
- # train with Adversarial Examples(AdvProp)
- # check more details in paper(Adversarial Examples Improve Image Recognition)
- url_map_advprop = {
- 'efficientnet-b0': 'https://github.com/lukemelas/EfficientNet-PyTorch/releases/download/1.0/adv-efficientnet-b0-b64d5a18.pth',
- 'efficientnet-b1': 'https://github.com/lukemelas/EfficientNet-PyTorch/releases/download/1.0/adv-efficientnet-b1-0f3ce85a.pth',
- 'efficientnet-b2': 'https://github.com/lukemelas/EfficientNet-PyTorch/releases/download/1.0/adv-efficientnet-b2-6e9d97e5.pth',
- 'efficientnet-b3': 'https://github.com/lukemelas/EfficientNet-PyTorch/releases/download/1.0/adv-efficientnet-b3-cdd7c0f4.pth',
- 'efficientnet-b4': 'https://github.com/lukemelas/EfficientNet-PyTorch/releases/download/1.0/adv-efficientnet-b4-44fb3a87.pth',
- 'efficientnet-b5': 'https://github.com/lukemelas/EfficientNet-PyTorch/releases/download/1.0/adv-efficientnet-b5-86493f6b.pth',
- 'efficientnet-b6': 'https://github.com/lukemelas/EfficientNet-PyTorch/releases/download/1.0/adv-efficientnet-b6-ac80338e.pth',
- 'efficientnet-b7': 'https://github.com/lukemelas/EfficientNet-PyTorch/releases/download/1.0/adv-efficientnet-b7-4652b6dd.pth',
- 'efficientnet-b8': 'https://github.com/lukemelas/EfficientNet-PyTorch/releases/download/1.0/adv-efficientnet-b8-22a8fe65.pth',
- }
- # TODO: add the petrained weights url map of 'efficientnet-l2'
- def load_pretrained_weights(model, model_name, weights_path=None, load_fc=True, advprop=False, verbose=True):
- """Loads pretrained weights from weights path or download using url.
- Args:
- model (Module): The whole model of efficientnet.
- model_name (str): Model name of efficientnet.
- weights_path (None or str):
- str: path to pretrained weights file on the local disk.
- None: use pretrained weights downloaded from the Internet.
- load_fc (bool): Whether to load pretrained weights for fc layer at the end of the model.
- advprop (bool): Whether to load pretrained weights
- trained with advprop (valid when weights_path is None).
- """
- if isinstance(weights_path, str):
- state_dict = torch.load(weights_path)
- else:
- # AutoAugment or Advprop (different preprocessing)
- url_map_ = url_map_advprop if advprop else url_map
- state_dict = model_zoo.load_url(url_map_[model_name])
- if load_fc:
- ret = model.load_state_dict(state_dict, strict=False)
- assert not ret.missing_keys, 'Missing keys when loading pretrained weights: {}'.format(ret.missing_keys)
- else:
- state_dict.pop('_fc.weight')
- state_dict.pop('_fc.bias')
- ret = model.load_state_dict(state_dict, strict=False)
- assert set(ret.missing_keys) == set(
- ['_fc.weight', '_fc.bias']), 'Missing keys when loading pretrained weights: {}'.format(ret.missing_keys)
- assert not ret.unexpected_keys, 'Missing keys when loading pretrained weights: {}'.format(ret.unexpected_keys)
- if verbose:
- print('Loaded pretrained weights for {}'.format(model_name))
- VALID_MODELS = (
- 'efficientnet-b0', 'efficientnet-b1', 'efficientnet-b2', 'efficientnet-b3',
- 'efficientnet-b4', 'efficientnet-b5', 'efficientnet-b6', 'efficientnet-b7',
- 'efficientnet-b8',
- # Support the construction of 'efficientnet-l2' without pretrained weights
- 'efficientnet-l2'
- )
- class MBConvBlock(nn.Module):
- """Mobile Inverted Residual Bottleneck Block.
- Args:
- block_args (namedtuple): BlockArgs, defined in utils.py.
- global_params (namedtuple): GlobalParam, defined in utils.py.
- image_size (tuple or list): [image_height, image_width].
- References:
- [1] https://arxiv.org/abs/1704.04861 (MobileNet v1)
- [2] https://arxiv.org/abs/1801.04381 (MobileNet v2)
- [3] https://arxiv.org/abs/1905.02244 (MobileNet v3)
- """
- def __init__(self, block_args, global_params, image_size=None):
- super().__init__()
- self._block_args = block_args
- self._bn_mom = 1 - global_params.batch_norm_momentum # pytorch's difference from tensorflow
- self._bn_eps = global_params.batch_norm_epsilon
- self.has_se = (self._block_args.se_ratio is not None) and (0 < self._block_args.se_ratio <= 1)
- self.id_skip = block_args.id_skip # whether to use skip connection and drop connect
- # Expansion phase (Inverted Bottleneck)
- inp = self._block_args.input_filters # number of input channels
- oup = self._block_args.input_filters * self._block_args.expand_ratio # number of output channels
- if self._block_args.expand_ratio != 1:
- Conv2d = get_same_padding_conv2d(image_size=image_size)
- self._expand_conv = Conv2d(in_channels=inp, out_channels=oup, kernel_size=1, bias=False)
- self._bn0 = nn.BatchNorm2d(num_features=oup, momentum=self._bn_mom, eps=self._bn_eps)
- # image_size = calculate_output_image_size(image_size, 1) <-- this wouldn't modify image_size
- # Depthwise convolution phase
- k = self._block_args.kernel_size
- s = self._block_args.stride
- Conv2d = get_same_padding_conv2d(image_size=image_size)
- self._depthwise_conv = Conv2d(
- in_channels=oup, out_channels=oup, groups=oup, # groups makes it depthwise
- kernel_size=k, stride=s, bias=False)
- self._bn1 = nn.BatchNorm2d(num_features=oup, momentum=self._bn_mom, eps=self._bn_eps)
- image_size = calculate_output_image_size(image_size, s)
- # Squeeze and Excitation layer, if desired
- if self.has_se:
- Conv2d = get_same_padding_conv2d(image_size=(1, 1))
- num_squeezed_channels = max(1, int(self._block_args.input_filters * self._block_args.se_ratio))
- self._se_reduce = Conv2d(in_channels=oup, out_channels=num_squeezed_channels, kernel_size=1)
- self._se_expand = Conv2d(in_channels=num_squeezed_channels, out_channels=oup, kernel_size=1)
- # Pointwise convolution phase
- final_oup = self._block_args.output_filters
- Conv2d = get_same_padding_conv2d(image_size=image_size)
- self._project_conv = Conv2d(in_channels=oup, out_channels=final_oup, kernel_size=1, bias=False)
- self._bn2 = nn.BatchNorm2d(num_features=final_oup, momentum=self._bn_mom, eps=self._bn_eps)
- self._swish = MemoryEfficientSwish()
- def forward(self, inputs, drop_connect_rate=None):
- """MBConvBlock's forward function.
- Args:
- inputs (tensor): Input tensor.
- drop_connect_rate (bool): Drop connect rate (float, between 0 and 1).
- Returns:
- Output of this block after processing.
- """
- # Expansion and Depthwise Convolution
- x = inputs
- if self._block_args.expand_ratio != 1:
- x = self._expand_conv(inputs)
- x = self._bn0(x)
- x = self._swish(x)
- x = self._depthwise_conv(x)
- x = self._bn1(x)
- x = self._swish(x)
- # Squeeze and Excitation
- if self.has_se:
- x_squeezed = F.adaptive_avg_pool2d(x, 1)
- x_squeezed = self._se_reduce(x_squeezed)
- x_squeezed = self._swish(x_squeezed)
- x_squeezed = self._se_expand(x_squeezed)
- x = torch.sigmoid(x_squeezed) * x
- # Pointwise Convolution
- x = self._project_conv(x)
- x = self._bn2(x)
- # Skip connection and drop connect
- input_filters, output_filters = self._block_args.input_filters, self._block_args.output_filters
- if self.id_skip and self._block_args.stride == 1 and input_filters == output_filters:
- # The combination of skip connection and drop connect brings about stochastic depth.
- if drop_connect_rate:
- x = drop_connect(x, p=drop_connect_rate, training=self.training)
- x = x + inputs # skip connection
- return x
- def set_swish(self, memory_efficient=True):
- """Sets swish function as memory efficient (for training) or standard (for export).
- Args:
- memory_efficient (bool): Whether to use memory-efficient version of swish.
- """
- self._swish = MemoryEfficientSwish() if memory_efficient else Swish()
- class EfficientNet(nn.Module):
- def __init__(self,blocks_args=None, global_params=None, factor=0.5, depth_factor=0.5):
- super().__init__()
- assert isinstance(blocks_args, list), 'blocks_args should be a list'
- assert len(blocks_args) > 0, 'block args must be greater than 0'
- new_blocks_args = []
- for block in blocks_args:
- new_block = BlockArgs(
- num_repeat=max(1, int(block.num_repeat * depth_factor)),
- kernel_size=block.kernel_size,
- stride=block.stride,
- expand_ratio=block.expand_ratio,
- input_filters=int(block.input_filters * factor),
- output_filters=int(block.output_filters * factor),
- se_ratio=block.se_ratio,
- id_skip=block.id_skip
- )
- new_blocks_args.append(new_block)
- channel = int(32 * factor)
- # 将新的列表替换掉原来的 blocks_args
- blocks_args = new_blocks_args
- self._global_params = global_params
- self._blocks_args = blocks_args
- # Batch norm parameters
- bn_mom = 1 - self._global_params.batch_norm_momentum
- bn_eps = self._global_params.batch_norm_epsilon
- # Get stem static or dynamic convolution depending on image size
- image_size = global_params.image_size
- Conv2d = get_same_padding_conv2d(image_size=image_size)
- # Stem
- in_channels = 3 # rgb
- out_channels = round_filters(channel, self._global_params) # number of output channels
- self._conv_stem = Conv2d(in_channels, out_channels, kernel_size=3, stride=2, bias=False)
- self._bn0 = nn.BatchNorm2d(num_features=out_channels, momentum=bn_mom, eps=bn_eps)
- image_size = calculate_output_image_size(image_size, 2)
- # Build blocks
- self._blocks = nn.ModuleList([])
- for block_args in self._blocks_args:
- # Update block input and output filters based on depth multiplier.
- block_args = block_args._replace(
- input_filters=round_filters(block_args.input_filters, self._global_params),
- output_filters=round_filters(block_args.output_filters, self._global_params),
- num_repeat=round_repeats(block_args.num_repeat, self._global_params)
- )
- # The first block needs to take care of stride and filter size increase.
- self._blocks.append(MBConvBlock(block_args, self._global_params, image_size=image_size))
- image_size = calculate_output_image_size(image_size, block_args.stride)
- if block_args.num_repeat > 1: # modify block_args to keep same output size
- block_args = block_args._replace(input_filters=block_args.output_filters, stride=1)
- for _ in range(block_args.num_repeat - 1):
- self._blocks.append(MBConvBlock(block_args, self._global_params, image_size=image_size))
- # image_size = calculate_output_image_size(image_size, block_args.stride) # stride = 1
- # Head
- in_channels = block_args.output_filters # output of final block
- out_channels = round_filters(1280, self._global_params)
- Conv2d = get_same_padding_conv2d(image_size=image_size)
- self._conv_head = Conv2d(in_channels, out_channels, kernel_size=1, bias=False)
- self._bn1 = nn.BatchNorm2d(num_features=out_channels, momentum=bn_mom, eps=bn_eps)
- # Final linear layer
- self._avg_pooling = nn.AdaptiveAvgPool2d(1)
- if self._global_params.include_top:
- self._dropout = nn.Dropout(self._global_params.dropout_rate)
- self._fc = nn.Linear(out_channels, self._global_params.num_classes)
- # set activation to memory efficient swish by default
- self._swish = MemoryEfficientSwish()
- self.width_list = [i.size(1) for i in self.forward(torch.randn(1, 3, 640, 640))]
- def set_swish(self, memory_efficient=True):
- """Sets swish function as memory efficient (for training) or standard (for export).
- Args:
- memory_efficient (bool): Whether to use memory-efficient version of swish.
- """
- self._swish = MemoryEfficientSwish() if memory_efficient else Swish()
- for block in self._blocks:
- block.set_swish(memory_efficient)
- def extract_endpoints(self, inputs):
- # """Use convolution layer to extract features
- # from reduction levels i in [1, 2, 3, 4, 5].
- #
- # Args:
- # inputs (tensor): Input tensor.
- #
- # Returns:
- # Dictionary of last intermediate features
- # with reduction levels i in [1, 2, 3, 4, 5].
- # Example:
- # >>> import torch
- # >>> from efficientnet.model import EfficientNet
- # >>> inputs = torch.rand(1, 3, 224, 224)
- # >>> model = EfficientNet.from_pretrained('efficientnet-b0')
- # >>> endpoints = model.extract_endpoints(inputs)
- # >>> print(endpoints['reduction_1'].shape) # torch.Size([1, 16, 112, 112])
- # >>> print(endpoints['reduction_2'].shape) # torch.Size([1, 24, 56, 56])
- # >>> print(endpoints['reduction_3'].shape) # torch.Size([1, 40, 28, 28])
- # >>> print(endpoints['reduction_4'].shape) # torch.Size([1, 112, 14, 14])
- # >>> print(endpoints['reduction_5'].shape) # torch.Size([1, 320, 7, 7])
- # >>> print(endpoints['reduction_6'].shape) # torch.Size([1, 1280, 7, 7])
- # """
- endpoints = dict()
- # Stem
- x = self._swish(self._bn0(self._conv_stem(inputs)))
- prev_x = x
- # Blocks
- for idx, block in enumerate(self._blocks):
- drop_connect_rate = self._global_params.drop_connect_rate
- if drop_connect_rate:
- drop_connect_rate *= float(idx) / len(self._blocks) # scale drop connect_rate
- x = block(x, drop_connect_rate=drop_connect_rate)
- if prev_x.size(2) > x.size(2):
- endpoints['reduction_{}'.format(len(endpoints) + 1)] = prev_x
- elif idx == len(self._blocks) - 1:
- endpoints['reduction_{}'.format(len(endpoints) + 1)] = x
- prev_x = x
- # Head
- x = self._swish(self._bn1(self._conv_head(x)))
- endpoints['reduction_{}'.format(len(endpoints) + 1)] = x
- return endpoints
- def forward(self, inputs):
- """use convolution layer to extract feature .
- Args:
- inputs (tensor): Input tensor.
- Returns:
- Output of the final convolution
- layer in the efficientnet model.
- """
- # Stem
- x = self._swish(self._bn0(self._conv_stem(inputs)))
- unique_tensors = {}
- # Blocks
- for idx, block in enumerate(self._blocks):
- drop_connect_rate = self._global_params.drop_connect_rate
- if drop_connect_rate:
- drop_connect_rate *= float(idx) / len(self._blocks) # scale drop connect_rate
- x = block(x, drop_connect_rate=drop_connect_rate)
- width, height = x.shape[2], x.shape[3]
- unique_tensors[(width, height)] = x
- result_list = list(unique_tensors.values())[-4:]
- # Head
- return result_list
- @classmethod
- def from_name(cls, model_name, in_channels=3, **override_params):
- """Create an efficientnet model according to name.
- Args:
- model_name (str): Name for efficientnet.
- in_channels (int): Input data's channel number.
- override_params (other key word params):
- Params to override model's global_params.
- Optional key:
- 'width_coefficient', 'depth_coefficient',
- 'image_size', 'dropout_rate',
- 'num_classes', 'batch_norm_momentum',
- 'batch_norm_epsilon', 'drop_connect_rate',
- 'depth_divisor', 'min_depth'
- Returns:
- An efficientnet model.
- """
- cls._check_model_name_is_valid(model_name)
- blocks_args, global_params = get_model_params(model_name, override_params)
- model = cls(blocks_args, global_params)
- model._change_in_channels(in_channels)
- return model
- @classmethod
- def from_pretrained(cls, model_name, weights_path=None, advprop=False,
- in_channels=3, num_classes=1000, **override_params):
- """Create an efficientnet model according to name.
- Args:
- model_name (str): Name for efficientnet.
- weights_path (None or str):
- str: path to pretrained weights file on the local disk.
- None: use pretrained weights downloaded from the Internet.
- advprop (bool):
- Whether to load pretrained weights
- trained with advprop (valid when weights_path is None).
- in_channels (int): Input data's channel number.
- num_classes (int):
- Number of categories for classification.
- It controls the output size for final linear layer.
- override_params (other key word params):
- Params to override model's global_params.
- Optional key:
- 'width_coefficient', 'depth_coefficient',
- 'image_size', 'dropout_rate',
- 'batch_norm_momentum',
- 'batch_norm_epsilon', 'drop_connect_rate',
- 'depth_divisor', 'min_depth'
- Returns:
- A pretrained efficientnet model.
- """
- model = cls.from_name(model_name, num_classes=num_classes, **override_params)
- load_pretrained_weights(model, model_name, weights_path=weights_path,
- load_fc=(num_classes == 1000), advprop=advprop)
- model._change_in_channels(in_channels)
- return model
- @classmethod
- def get_image_size(cls, model_name):
- """Get the input image size for a given efficientnet model.
- Args:
- model_name (str): Name for efficientnet.
- Returns:
- Input image size (resolution).
- """
- cls._check_model_name_is_valid(model_name)
- _, _, res, _ = efficientnet_params(model_name)
- return res
- @classmethod
- def _check_model_name_is_valid(cls, model_name):
- """Validates model name.
- Args:
- model_name (str): Name for efficientnet.
- Returns:
- bool: Is a valid name or not.
- """
- if model_name not in VALID_MODELS:
- raise ValueError('model_name should be one of: ' + ', '.join(VALID_MODELS))
- def _change_in_channels(self, in_channels):
- """Adjust model's first convolution layer to in_channels, if in_channels not equals 3.
- Args:
- in_channels (int): Input data's channel number.
- """
- if in_channels != 3:
- Conv2d = get_same_padding_conv2d(image_size=self._global_params.image_size)
- out_channels = round_filters(32, self._global_params)
- self._conv_stem = Conv2d(in_channels, out_channels, kernel_size=3, stride=2, bias=False)
- def efficient(model_name='efficientnet-b0', factor=0.25, depth_factor=0.5, pretrained=False):
- if pretrained:
- model = EfficientNet.from_pretrained('{}'.format(model_name, factor=factor, depth_factor=depth_factor))
- else:
- model = EfficientNet.from_name('{}'.format(model_name, factor=factor, depth_factor=depth_factor))
- return model
- if __name__ == "__main__":
- # VALID_MODELS = (
- # 'efficientnet-b0', 'efficientnet-b1', 'efficientnet-b2', 'efficientnet-b3',
- # 'efficientnet-b4', 'efficientnet-b5', 'efficientnet-b6', 'efficientnet-b7',
- # 'efficientnet-b8',
- # # Support the construction of 'efficientnet-l2' without pretrained weights
- # 'efficientnet-l2'
- # )
- # Generating Sample image
- image_size = (1, 3, 640, 640)
- image = torch.rand(*image_size)
- # Model
- model = efficient('efficientnet-b0', factor=0.25, depth_factor=0.5)
- out = model(image)
- print(len(out))
四、手把手教你添加EfficientNetV1机制
4.1 修改一
第一步还是建立文件,我们找到如下ultralytics/nn文件夹下建立一个目录名字呢就是'Addmodules'文件夹( 用群内的文件的话已经有了无需新建) !然后在其内部建立一个新的py文件将核心代码复制粘贴进去即可

4.2 修改二
第二步我们在该目录下创建一个新的py文件名字为'__init__.py'( 用群内的文件的话已经有了无需新建) ,然后在其内部导入我们的检测头如下图所示。

4.3 修改三
第三步我门中到如下文件'ultralytics/nn/tasks.py'进行导入和注册我们的模块( 用群内的文件的话已经有了无需重新导入直接开始第四步即可) !
从今天开始以后的教程就都统一成这个样子了,因为我默认大家用了我群内的文件来进行修改!!
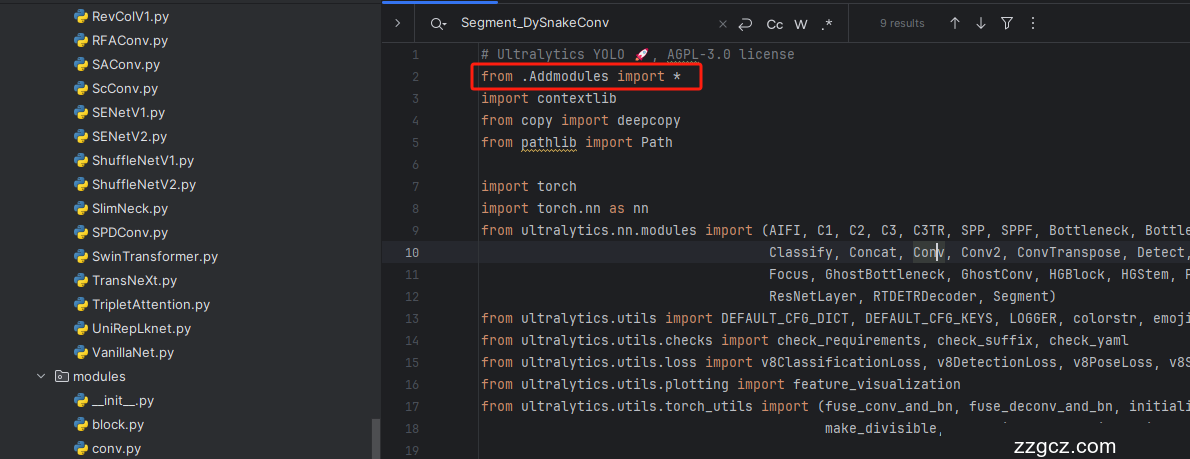
4.4 修改四
添加如下两行代码!!!

4.5 修改五
找到七百多行大概把具体看图片,按照图片来修改就行,添加红框内的部分,注意没有()只是 函数 名。

- elif m in {自行添加对应的模型即可,下面都是一样的}:
- m = m(*args)
- c2 = m.width_list # 返回通道列表
- backbone = True
4.6 修改六
下面的两个红框内都是需要改动的。

- if isinstance(c2, list):
- m_ = m
- m_.backbone = True
- else:
- m_ = nn.Sequential(*(m(*args) for _ in range(n))) if n > 1 else m(*args) # module
- t = str(m)[8:-2].replace('__main__.', '') # module type
- m.np = sum(x.numel() for x in m_.parameters()) # number params
- m_.i, m_.f, m_.type = i + 4 if backbone else i, f, t # attach index, 'from' index, type
4.7 修改七
如下的也需要修改,全部按照我的来。

代码如下把原先的代码替换了即可。
- if verbose:
- LOGGER.info(f'{i:>3}{str(f):>20}{n_:>3}{m.np:10.0f} {t:<45}{str(args):<30}') # print
- save.extend(x % (i + 4 if backbone else i) for x in ([f] if isinstance(f, int) else f) if x != -1) # append to savelist
- layers.append(m_)
- if i == 0:
- ch = []
- if isinstance(c2, list):
- ch.extend(c2)
- if len(c2) != 5:
- ch.insert(0, 0)
- else:
- ch.append(c2)
4.8 修改八
修改八和前面的都不太一样,需要修改前向传播中的一个部分, 已经离开了parse_model方法了。
可以在图片中开代码行数,没有离开task.py文件都是同一个文件。 同时这个部分有好几个前向传播都很相似,大家不要看错了, 是70多行左右的!!!,同时我后面提供了代码,大家直接复制粘贴即可,有时间我针对这里会出一个视频。

代码如下->
- def _predict_once(self, x, profile=False, visualize=False, embed=None):
- """
- Perform a forward pass through the network.
- Args:
- x (torch.Tensor): The input tensor to the model.
- profile (bool): Print the computation time of each layer if True, defaults to False.
- visualize (bool): Save the feature maps of the model if True, defaults to False.
- embed (list, optional): A list of feature vectors/embeddings to return.
- Returns:
- (torch.Tensor): The last output of the model.
- """
- y, dt, embeddings = [], [], [] # outputs
- for m in self.model:
- if m.f != -1: # if not from previous layer
- x = y[m.f] if isinstance(m.f, int) else [x if j == -1 else y[j] for j in m.f] # from earlier layers
- if profile:
- self._profile_one_layer(m, x, dt)
- if hasattr(m, 'backbone'):
- x = m(x)
- if len(x) != 5: # 0 - 5
- x.insert(0, None)
- for index, i in enumerate(x):
- if index in self.save:
- y.append(i)
- else:
- y.append(None)
- x = x[-1] # 最后一个输出传给下一层
- else:
- x = m(x) # run
- y.append(x if m.i in self.save else None) # save output
- if visualize:
- feature_visualization(x, m.type, m.i, save_dir=visualize)
- if embed and m.i in embed:
- embeddings.append(nn.functional.adaptive_avg_pool2d(x, (1, 1)).squeeze(-1).squeeze(-1)) # flatten
- if m.i == max(embed):
- return torch.unbind(torch.cat(embeddings, 1), dim=0)
- return x
到这里就完成了修改部分,但是这里面细节很多,大家千万要注意不要替换多余的代码,导致报错,也不要拉下任何一部,都会导致运行失败,而且报错很难排查!!!很难排查!!!
注意!!! 额外的修改!
关注我的其实都知道,我大部分的修改都是一样的,这个网络需要额外的修改一步,就是s一个参数,将下面的s改为640!!!即可完美运行!!

打印计算量问题解决方案
我们找到如下文件'ultralytics/utils/torch_utils.py'按照如下的图片进行修改,否则容易打印不出来计算量。

注意事项!!!
如果大家在验证的时候报错形状不匹配的错误可以固定验证集的图片尺寸,方法如下 ->
找到下面这个文件ultralytics/ models /yolo/detect/train.py然后其中有一个类是DetectionTrainer class中的build_dataset函数中的一个参数rect=mode == 'val'改为rect=False

五、EfficientNetV1的yaml文件
复制如下yaml文件进行运行!!!
5.1 EfficientNetV1 的yaml文件版本
此版本训练信息:YOLO11-EfficientNetV1 summary: 337 layers, 3,515,595 parameters, 3,515,579 gradients, 3.7 GFLOPs
使用说明:# 下面 [-1, 1, efficientnet-b0}, [efficientnet-b0, 0.25,0.5]] 参数位置的0.25是通道放缩的系数, YOLOv11N是0.25 YOLOv11S是0.5 YOLOv11M是1. YOLOv11l是1 YOLOv11是1.5大家根据自己训练的YOLO版本设定即可.
# 0.5对应的是模型的深度系数
# efficientnet-b0为模型的版本
# 本文支持版本有
# 'efficientnet-b0', 'efficientnet-b1', 'efficientnet-b2', 'efficientnet-b3', # 'efficientnet-b4', 'efficientnet-b5', 'efficientnet-b6', 'efficientnet-b7', # 'efficientnet-b8', 'efficientnet-l2'
- # Ultralytics YOLO 🚀, AGPL-3.0 license
- # YOLO11 object detection model with P3-P5 outputs. For Usage examples see https://docs.ultralytics.com/tasks/detect
- # Parameters
- nc: 80 # number of classes
- scales: # model compound scaling constants, i.e. 'model=yolo11n.yaml' will call yolo11.yaml with scale 'n'
- # [depth, width, max_channels]
- n: [0.50, 0.25, 1024] # summary: 319 layers, 2624080 parameters, 2624064 gradients, 6.6 GFLOPs
- s: [0.50, 0.50, 1024] # summary: 319 layers, 9458752 parameters, 9458736 gradients, 21.7 GFLOPs
- m: [0.50, 1.00, 512] # summary: 409 layers, 20114688 parameters, 20114672 gradients, 68.5 GFLOPs
- l: [1.00, 1.00, 512] # summary: 631 layers, 25372160 parameters, 25372144 gradients, 87.6 GFLOPs
- x: [1.00, 1.50, 512] # summary: 631 layers, 56966176 parameters, 56966160 gradients, 196.0 GFLOPs
- # 下面 [-1, 1, efficientnet-b0}, [efficientnet-b0, 0.25,0.5]] 参数位置的0.25是通道放缩的系数, YOLOv11N是0.25 YOLOv11S是0.5 YOLOv11M是1. YOLOv11l是1 YOLOv11是1.5大家根据自己训练的YOLO版本设定即可.
- # 0.5对应的是模型的深度系数
- # efficientnet-b0为模型的版本
- # 支持的版本:
- # 'efficientnet-b0', 'efficientnet-b1', 'efficientnet-b2', 'efficientnet-b3',
- # 'efficientnet-b4', 'efficientnet-b5', 'efficientnet-b6', 'efficientnet-b7',
- # 'efficientnet-b8', 'efficientnet-l2'
- # YOLO11n backbone
- backbone:
- # [from, repeats, module, args]
- - [-1, 1, efficient, [efficientnet-b0, 0.25,0.5]] # 0-4 P1/2
- - [-1, 1, SPPF, [1024, 5]] # 5
- - [-1, 2, C2PSA, [1024]] # 6
- # YOLO11n head
- head:
- - [-1, 1, nn.Upsample, [None, 2, "nearest"]]
- - [[-1, 3], 1, Concat, [1]] # cat backbone P4
- - [-1, 2, C3k2, [512, False]] # 9
- - [-1, 1, nn.Upsample, [None, 2, "nearest"]]
- - [[-1, 2], 1, Concat, [1]] # cat backbone P3
- - [-1, 2, C3k2, [256, False]] # 12 (P3/8-small)
- - [-1, 1, Conv, [256, 3, 2]]
- - [[-1, 9], 1, Concat, [1]] # cat head P4
- - [-1, 2, C3k2, [512, False]] # 15 (P4/16-medium)
- - [-1, 1, Conv, [512, 3, 2]]
- - [[-1, 6], 1, Concat, [1]] # cat head P5
- - [-1, 2, C3k2, [1024, True]] # 18 (P5/32-large)
- - [[12, 15, 18], 1, Detect, [nc]] # Detect(P3, P4, P5)
5.2 训练文件
- import warnings
- warnings.filterwarnings('ignore')
- from ultralytics import YOLO
- if __name__ == '__main__':
- model = YOLO('ultralytics/cfg/models/v8/yolov8-C2f-FasterBlock.yaml')
- # model.load('yolov8n.pt') # loading pretrain weights
- model.train(data=r'替换数据集yaml文件地址',
- # 如果大家任务是其它的'ultralytics/cfg/default.yaml'找到这里修改task可以改成detect, segment, classify, pose
- cache=False,
- imgsz=640,
- epochs=150,
- single_cls=False, # 是否是单类别检测
- batch=4,
- close_mosaic=10,
- workers=0,
- device='0',
- optimizer='SGD', # using SGD
- # resume='', # 如过想续训就设置last.pt的地址
- amp=False, # 如果出现训练损失为Nan可以关闭amp
- project='runs/train',
- name='exp',
- )
六、成功运行记录
下面是成功运行的截图,已经完成了有1个epochs的训练,图片太大截不全第2个epochs,这里改完之后打印出了点问题,但是不影响任何功能,后期我找时间修复一下这个问题。

七、本文总M结
到此本文的正式分享内容就结束了,在这里给大家推荐我的YOLOv11改进有效涨点专栏,本专栏目前为新开的平均质量分98分,后期我会根据各种最新的前沿顶会进行论文复现,也会对一些老的改进机制进行补充, 目前本专栏免费阅读(暂时,大家尽早关注不迷路~) ,如果大家觉得本文帮助到你了,订阅本专栏,关注后续更多的更新~
