一、本文介绍
本文给大家带来的最新改进机制是融合改进,利用 Damo-YOLO 配合 SwinTransformer ,其中Damo- YOLO 和 SwinTransformer 在我前面的文章都已经讲过了如何使用,本文主要讲一下将他们融合起来的注意事项以及使用方法,同时在开始讲解之前推荐一下我的专栏,本专栏的内容支持(分类、检测、分割、追踪、 关键点检测 ),专栏目前为限时折扣 (相同文章数量全网最低) , 欢迎大家订阅本专栏,本专栏每周更新3-5篇最新机制,更有包含我所有改进的文件和交流群提供给大家, 本文的SwinTransformer可以替换为本专栏的20余种主干。
欢迎大家订阅我的专栏一起学习YOLO!
| 训练信息:YOLO11-SwinTransformer-RepGFPN summary: 353 layers, 2,736,687 parameters, 2,736,671 gradients, 6.3 GFLOPs |
| 基础版本:YOLO11 summary: 319 layers, 2,591,010 parameters, 2,590,994 gradients, 6.4 GFLOPs |
二、原理介绍
这部分就不复制过来了,大家想看的可以去对应文章找。
Damo-YOLO: Damo-YOLO的地址
Swintransformer: YOLOv11改进 | 主干/Backbone篇 | 视觉变换器SwinTransformer目标检测网络( 适配yolov11全系列模型)_yolov11代码-CSDN博客
三、Damo-YOLO核心代码使用方式
下面的代码是GFPN的核心代码,我们将其复制导' ultralytics /nn'目录下,在其中创建一个文件,我这里起名为GFPN然后粘贴进去,其余使用方式看后面。
- import torch
- import torch.nn as nn
- import numpy as np
- class swish(nn.Module):
- def forward(self, x):
- return x * torch.sigmoid(x)
- def autopad(k, p=None, d=1): # kernel, padding, dilation
- """Pad to 'same' shape outputs."""
- if d > 1:
- k = d * (k - 1) + 1 if isinstance(k, int) else [d * (x - 1) + 1 for x in k] # actual kernel-size
- if p is None:
- p = k // 2 if isinstance(k, int) else [x // 2 for x in k] # auto-pad
- return p
- class Conv(nn.Module):
- """Standard convolution with args(ch_in, ch_out, kernel, stride, padding, groups, dilation, activation)."""
- default_act = swish() # default activation
- def __init__(self, c1, c2, k=1, s=1, p=None, g=1, d=1, act=True):
- """Initialize Conv layer with given arguments including activation."""
- super().__init__()
- self.conv = nn.Conv2d(c1, c2, k, s, autopad(k, p, d), groups=g, dilation=d, bias=False)
- self.bn = nn.BatchNorm2d(c2)
- self.act = self.default_act if act is True else act if isinstance(act, nn.Module) else nn.Identity()
- def forward(self, x):
- """Apply convolution, batch normalization and activation to input tensor."""
- return self.act(self.bn(self.conv(x)))
- def forward_fuse(self, x):
- """Perform transposed convolution of 2D data."""
- return self.act(self.conv(x))
- class RepConv(nn.Module):
- default_act = swish() # default activation
- def __init__(self, c1, c2, k=3, s=1, p=1, g=1, d=1, act=True, bn=False, deploy=False):
- """Initializes Light Convolution layer with inputs, outputs & optional activation function."""
- super().__init__()
- assert k == 3 and p == 1
- self.g = g
- self.c1 = c1
- self.c2 = c2
- self.act = self.default_act if act is True else act if isinstance(act, nn.Module) else nn.Identity()
- self.bn = nn.BatchNorm2d(num_features=c1) if bn and c2 == c1 and s == 1 else None
- self.conv1 = Conv(c1, c2, k, s, p=p, g=g, act=False)
- self.conv2 = Conv(c1, c2, 1, s, p=(p - k // 2), g=g, act=False)
- def forward_fuse(self, x):
- """Forward process."""
- return self.act(self.conv(x))
- def forward(self, x):
- """Forward process."""
- id_out = 0 if self.bn is None else self.bn(x)
- return self.act(self.conv1(x) + self.conv2(x) + id_out)
- def get_equivalent_kernel_bias(self):
- """Returns equivalent kernel and bias by adding 3x3 kernel, 1x1 kernel and identity kernel with their biases."""
- kernel3x3, bias3x3 = self._fuse_bn_tensor(self.conv1)
- kernel1x1, bias1x1 = self._fuse_bn_tensor(self.conv2)
- kernelid, biasid = self._fuse_bn_tensor(self.bn)
- return kernel3x3 + self._pad_1x1_to_3x3_tensor(kernel1x1) + kernelid, bias3x3 + bias1x1 + biasid
- def _pad_1x1_to_3x3_tensor(self, kernel1x1):
- """Pads a 1x1 tensor to a 3x3 tensor."""
- if kernel1x1 is None:
- return 0
- else:
- return torch.nn.functional.pad(kernel1x1, [1, 1, 1, 1])
- def _fuse_bn_tensor(self, branch):
- """Generates appropriate kernels and biases for convolution by fusing branches of the neural network."""
- if branch is None:
- return 0, 0
- if isinstance(branch, Conv):
- kernel = branch.conv.weight
- running_mean = branch.bn.running_mean
- running_var = branch.bn.running_var
- gamma = branch.bn.weight
- beta = branch.bn.bias
- eps = branch.bn.eps
- elif isinstance(branch, nn.BatchNorm2d):
- if not hasattr(self, 'id_tensor'):
- input_dim = self.c1 // self.g
- kernel_value = np.zeros((self.c1, input_dim, 3, 3), dtype=np.float32)
- for i in range(self.c1):
- kernel_value[i, i % input_dim, 1, 1] = 1
- self.id_tensor = torch.from_numpy(kernel_value).to(branch.weight.device)
- kernel = self.id_tensor
- running_mean = branch.running_mean
- running_var = branch.running_var
- gamma = branch.weight
- beta = branch.bias
- eps = branch.eps
- std = (running_var + eps).sqrt()
- t = (gamma / std).reshape(-1, 1, 1, 1)
- return kernel * t, beta - running_mean * gamma / std
- def fuse_convs(self):
- """Combines two convolution layers into a single layer and removes unused attributes from the class."""
- if hasattr(self, 'conv'):
- return
- kernel, bias = self.get_equivalent_kernel_bias()
- self.conv = nn.Conv2d(in_channels=self.conv1.conv.in_channels,
- out_channels=self.conv1.conv.out_channels,
- kernel_size=self.conv1.conv.kernel_size,
- stride=self.conv1.conv.stride,
- padding=self.conv1.conv.padding,
- dilation=self.conv1.conv.dilation,
- groups=self.conv1.conv.groups,
- bias=True).requires_grad_(False)
- self.conv.weight.data = kernel
- self.conv.bias.data = bias
- for para in self.parameters():
- para.detach_()
- self.__delattr__('conv1')
- self.__delattr__('conv2')
- if hasattr(self, 'nm'):
- self.__delattr__('nm')
- if hasattr(self, 'bn'):
- self.__delattr__('bn')
- if hasattr(self, 'id_tensor'):
- self.__delattr__('id_tensor')
- class BasicBlock_3x3_Reverse(nn.Module):
- def __init__(self,
- ch_in,
- ch_hidden_ratio,
- ch_out,
- shortcut=True):
- super(BasicBlock_3x3_Reverse, self).__init__()
- assert ch_in == ch_out
- ch_hidden = int(ch_in * ch_hidden_ratio)
- self.conv1 = Conv(ch_hidden, ch_out, 3, s=1)
- self.conv2 = RepConv(ch_in, ch_hidden, 3, s=1)
- self.shortcut = shortcut
- def forward(self, x):
- y = self.conv2(x)
- y = self.conv1(y)
- if self.shortcut:
- return x + y
- else:
- return y
- class SPP(nn.Module):
- def __init__(
- self,
- ch_in,
- ch_out,
- k,
- pool_size
- ):
- super(SPP, self).__init__()
- self.pool = []
- for i, size in enumerate(pool_size):
- pool = nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=size,
- stride=1,
- padding=size // 2,
- ceil_mode=False)
- self.add_module('pool{}'.format(i), pool)
- self.pool.append(pool)
- self.conv = Conv(ch_in, ch_out, k)
- def forward(self, x):
- outs = [x]
- for pool in self.pool:
- outs.append(pool(x))
- y = torch.cat(outs, axis=1)
- y = self.conv(y)
- return y
- class CSPStage(nn.Module):
- def __init__(self,
- ch_in,
- ch_out,
- n,
- block_fn='BasicBlock_3x3_Reverse',
- ch_hidden_ratio=1.0,
- act='silu',
- spp=False):
- super(CSPStage, self).__init__()
- split_ratio = 2
- ch_first = int(ch_out // split_ratio)
- ch_mid = int(ch_out - ch_first)
- self.conv1 = Conv(ch_in, ch_first, 1)
- self.conv2 = Conv(ch_in, ch_mid, 1)
- self.convs = nn.Sequential()
- next_ch_in = ch_mid
- for i in range(n):
- if block_fn == 'BasicBlock_3x3_Reverse':
- self.convs.add_module(
- str(i),
- BasicBlock_3x3_Reverse(next_ch_in,
- ch_hidden_ratio,
- ch_mid,
- shortcut=True))
- else:
- raise NotImplementedError
- if i == (n - 1) // 2 and spp:
- self.convs.add_module('spp', SPP(ch_mid * 4, ch_mid, 1, [5, 9, 13]))
- next_ch_in = ch_mid
- self.conv3 = Conv(ch_mid * n + ch_first, ch_out, 1)
- def forward(self, x):
- y1 = self.conv1(x)
- y2 = self.conv2(x)
- mid_out = [y1]
- for conv in self.convs:
- y2 = conv(y2)
- mid_out.append(y2)
- y = torch.cat(mid_out, axis=1)
- y = self.conv3(y)
- return y
3.1 修改一
第一还是建立文件,我们找到如下ultralytics/nn文件夹下建立一个目录名字呢就是'Addmodules'文件夹( 用群内的文件的话已经有了无需新建) !然后在其内部建立一个新的py文件将核心代码复制粘贴进去即可。

3.2 修改二
第二步我们在该目录下创建一个新的py文件名字为'__init__.py'( 用群内的文件的话已经有了无需新建) ,然后在其内部导入我们的检测头如下图所示。

3.3 修改三
第三步我门中到如下文件'ultralytics/nn/tasks.py'进行导入和注册我们的模块( 用群内的文件的话已经有了无需重新导入直接开始第四步即可) !
从今天开始以后的教程就都统一成这个样子了,因为我默认大家用了我群内的文件来进行修改!!
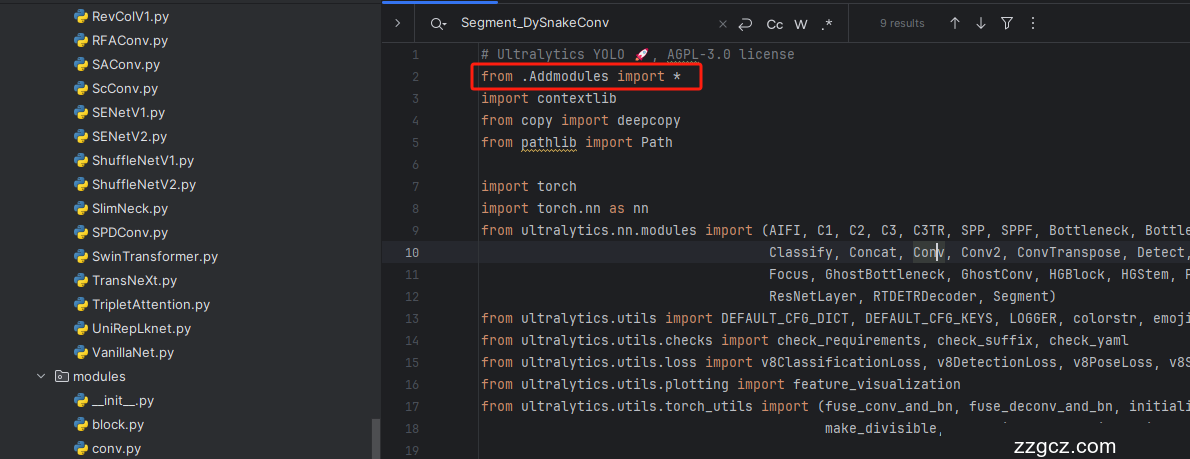
3.4 修改四
按照我的添加在parse_model里添加即可。

到此就修改完成了,大家可以复制下面的yaml文件运行。
四、 Swintransformer的核心代码和使用方式
Swintransformer的核心代码,使用方式看后面介绍。
- import torch
- import torch.nn as nn
- import torch.nn.functional as F
- import torch.utils.checkpoint as checkpoint
- import numpy as np
- from timm.models.layers import DropPath, to_2tuple, trunc_normal_
- __all__ = ['SwinTransformer']
- class Mlp(nn.Module):
- """ Multilayer perceptron."""
- def __init__(self, in_features, hidden_features=None, out_features=None, act_layer=nn.GELU, drop=0.):
- super().__init__()
- out_features = out_features or in_features
- hidden_features = hidden_features or in_features
- self.fc1 = nn.Linear(in_features, hidden_features)
- self.act = act_layer()
- self.fc2 = nn.Linear(hidden_features, out_features)
- self.drop = nn.Dropout(drop)
- def forward(self, x):
- x = self.fc1(x)
- x = self.act(x)
- x = self.drop(x)
- x = self.fc2(x)
- x = self.drop(x)
- return x
- def window_partition(x, window_size):
- """
- Args:
- x: (B, H, W, C)
- window_size (int): window size
- Returns:
- windows: (num_windows*B, window_size, window_size, C)
- """
- B, H, W, C = x.shape
- x = x.view(B, H // window_size, window_size, W // window_size, window_size, C)
- windows = x.permute(0, 1, 3, 2, 4, 5).contiguous().view(-1, window_size, window_size, C)
- return windows
- def window_reverse(windows, window_size, H, W):
- """
- Args:
- windows: (num_windows*B, window_size, window_size, C)
- window_size (int): Window size
- H (int): Height of image
- W (int): Width of image
- Returns:
- x: (B, H, W, C)
- """
- B = int(windows.shape[0] / (H * W / window_size / window_size))
- x = windows.view(B, H // window_size, W // window_size, window_size, window_size, -1)
- x = x.permute(0, 1, 3, 2, 4, 5).contiguous().view(B, H, W, -1)
- return x
- class WindowAttention(nn.Module):
- """ Window based multi-head self attention (W-MSA) module with relative position bias.
- It supports both of shifted and non-shifted window.
- Args:
- dim (int): Number of input channels.
- window_size (tuple[int]): The height and width of the window.
- num_heads (int): Number of attention heads.
- qkv_bias (bool, optional): If True, add a learnable bias to query, key, value. Default: True
- qk_scale (float | None, optional): Override default qk scale of head_dim ** -0.5 if set
- attn_drop (float, optional): Dropout ratio of attention weight. Default: 0.0
- proj_drop (float, optional): Dropout ratio of output. Default: 0.0
- """
- def __init__(self, dim, window_size, num_heads, qkv_bias=True, qk_scale=None, attn_drop=0., proj_drop=0.):
- super().__init__()
- self.dim = dim
- self.window_size = window_size # Wh, Ww
- self.num_heads = num_heads
- head_dim = dim // num_heads
- self.scale = qk_scale or head_dim ** -0.5
- # define a parameter table of relative position bias
- self.relative_position_bias_table = nn.Parameter(
- torch.zeros((2 * window_size[0] - 1) * (2 * window_size[1] - 1), num_heads)) # 2*Wh-1 * 2*Ww-1, nH
- # get pair-wise relative position index for each token inside the window
- coords_h = torch.arange(self.window_size[0])
- coords_w = torch.arange(self.window_size[1])
- coords = torch.stack(torch.meshgrid([coords_h, coords_w])) # 2, Wh, Ww
- coords_flatten = torch.flatten(coords, 1) # 2, Wh*Ww
- relative_coords = coords_flatten[:, :, None] - coords_flatten[:, None, :] # 2, Wh*Ww, Wh*Ww
- relative_coords = relative_coords.permute(1, 2, 0).contiguous() # Wh*Ww, Wh*Ww, 2
- relative_coords[:, :, 0] += self.window_size[0] - 1 # shift to start from 0
- relative_coords[:, :, 1] += self.window_size[1] - 1
- relative_coords[:, :, 0] *= 2 * self.window_size[1] - 1
- relative_position_index = relative_coords.sum(-1) # Wh*Ww, Wh*Ww
- self.register_buffer("relative_position_index", relative_position_index)
- self.qkv = nn.Linear(dim, dim * 3, bias=qkv_bias)
- self.attn_drop = nn.Dropout(attn_drop)
- self.proj = nn.Linear(dim, dim)
- self.proj_drop = nn.Dropout(proj_drop)
- trunc_normal_(self.relative_position_bias_table, std=.02)
- self.softmax = nn.Softmax(dim=-1)
- def forward(self, x, mask=None):
- """ Forward function.
- Args:
- x: input features with shape of (num_windows*B, N, C)
- mask: (0/-inf) mask with shape of (num_windows, Wh*Ww, Wh*Ww) or None
- """
- B_, N, C = x.shape
- qkv = self.qkv(x).reshape(B_, N, 3, self.num_heads, C // self.num_heads).permute(2, 0, 3, 1, 4)
- q, k, v = qkv[0], qkv[1], qkv[2] # make torchscript happy (cannot use tensor as tuple)
- q = q * self.scale
- attn = (q @ k.transpose(-2, -1))
- relative_position_bias = self.relative_position_bias_table[self.relative_position_index.view(-1)].view(
- self.window_size[0] * self.window_size[1], self.window_size[0] * self.window_size[1], -1) # Wh*Ww,Wh*Ww,nH
- relative_position_bias = relative_position_bias.permute(2, 0, 1).contiguous() # nH, Wh*Ww, Wh*Ww
- attn = attn + relative_position_bias.unsqueeze(0)
- if mask is not None:
- nW = mask.shape[0]
- attn = attn.view(B_ // nW, nW, self.num_heads, N, N) + mask.unsqueeze(1).unsqueeze(0)
- attn = attn.view(-1, self.num_heads, N, N)
- attn = self.softmax(attn)
- else:
- attn = self.softmax(attn)
- attn = self.attn_drop(attn)
- x = (attn @ v).transpose(1, 2).reshape(B_, N, C)
- x = self.proj(x)
- x = self.proj_drop(x)
- return x
- class SwinTransformerBlock(nn.Module):
- """ Swin Transformer Block.
- Args:
- dim (int): Number of input channels.
- num_heads (int): Number of attention heads.
- window_size (int): Window size.
- shift_size (int): Shift size for SW-MSA.
- mlp_ratio (float): Ratio of mlp hidden dim to embedding dim.
- qkv_bias (bool, optional): If True, add a learnable bias to query, key, value. Default: True
- qk_scale (float | None, optional): Override default qk scale of head_dim ** -0.5 if set.
- drop (float, optional): Dropout rate. Default: 0.0
- attn_drop (float, optional): Attention dropout rate. Default: 0.0
- drop_path (float, optional): Stochastic depth rate. Default: 0.0
- act_layer (nn.Module, optional): Activation layer. Default: nn.GELU
- norm_layer (nn.Module, optional): Normalization layer. Default: nn.LayerNorm
- """
- def __init__(self, dim, num_heads, window_size=7, shift_size=0,
- mlp_ratio=4., qkv_bias=True, qk_scale=None, drop=0., attn_drop=0., drop_path=0.,
- act_layer=nn.GELU, norm_layer=nn.LayerNorm):
- super().__init__()
- self.dim = dim
- self.num_heads = num_heads
- self.window_size = window_size
- self.shift_size = shift_size
- self.mlp_ratio = mlp_ratio
- assert 0 <= self.shift_size < self.window_size, "shift_size must in 0-window_size"
- self.norm1 = norm_layer(dim)
- self.attn = WindowAttention(
- dim, window_size=to_2tuple(self.window_size), num_heads=num_heads,
- qkv_bias=qkv_bias, qk_scale=qk_scale, attn_drop=attn_drop, proj_drop=drop)
- self.drop_path = DropPath(drop_path) if drop_path > 0. else nn.Identity()
- self.norm2 = norm_layer(dim)
- mlp_hidden_dim = int(dim * mlp_ratio)
- self.mlp = Mlp(in_features=dim, hidden_features=mlp_hidden_dim, act_layer=act_layer, drop=drop)
- self.H = None
- self.W = None
- def forward(self, x, mask_matrix):
- """ Forward function.
- Args:
- x: Input feature, tensor size (B, H*W, C).
- H, W: Spatial resolution of the input feature.
- mask_matrix: Attention mask for cyclic shift.
- """
- B, L, C = x.shape
- H, W = self.H, self.W
- assert L == H * W, "input feature has wrong size"
- shortcut = x
- x = self.norm1(x)
- x = x.view(B, H, W, C)
- # pad feature maps to multiples of window size
- pad_l = pad_t = 0
- pad_r = (self.window_size - W % self.window_size) % self.window_size
- pad_b = (self.window_size - H % self.window_size) % self.window_size
- x = F.pad(x, (0, 0, pad_l, pad_r, pad_t, pad_b))
- _, Hp, Wp, _ = x.shape
- # cyclic shift
- if self.shift_size > 0:
- shifted_x = torch.roll(x, shifts=(-self.shift_size, -self.shift_size), dims=(1, 2))
- attn_mask = mask_matrix.type(x.dtype)
- else:
- shifted_x = x
- attn_mask = None
- # partition windows
- x_windows = window_partition(shifted_x, self.window_size) # nW*B, window_size, window_size, C
- x_windows = x_windows.view(-1, self.window_size * self.window_size, C) # nW*B, window_size*window_size, C
- # W-MSA/SW-MSA
- attn_windows = self.attn(x_windows, mask=attn_mask) # nW*B, window_size*window_size, C
- # merge windows
- attn_windows = attn_windows.view(-1, self.window_size, self.window_size, C)
- shifted_x = window_reverse(attn_windows, self.window_size, Hp, Wp) # B H' W' C
- # reverse cyclic shift
- if self.shift_size > 0:
- x = torch.roll(shifted_x, shifts=(self.shift_size, self.shift_size), dims=(1, 2))
- else:
- x = shifted_x
- if pad_r > 0 or pad_b > 0:
- x = x[:, :H, :W, :].contiguous()
- x = x.view(B, H * W, C)
- # FFN
- x = shortcut + self.drop_path(x)
- x = x + self.drop_path(self.mlp(self.norm2(x)))
- return x
- class PatchMerging(nn.Module):
- """ Patch Merging Layer
- Args:
- dim (int): Number of input channels.
- norm_layer (nn.Module, optional): Normalization layer. Default: nn.LayerNorm
- """
- def __init__(self, dim, norm_layer=nn.LayerNorm):
- super().__init__()
- self.dim = dim
- self.reduction = nn.Linear(4 * dim, 2 * dim, bias=False)
- self.norm = norm_layer(4 * dim)
- def forward(self, x, H, W):
- """ Forward function.
- Args:
- x: Input feature, tensor size (B, H*W, C).
- H, W: Spatial resolution of the input feature.
- """
- B, L, C = x.shape
- assert L == H * W, "input feature has wrong size"
- x = x.view(B, H, W, C)
- # padding
- pad_input = (H % 2 == 1) or (W % 2 == 1)
- if pad_input:
- x = F.pad(x, (0, 0, 0, W % 2, 0, H % 2))
- x0 = x[:, 0::2, 0::2, :] # B H/2 W/2 C
- x1 = x[:, 1::2, 0::2, :] # B H/2 W/2 C
- x2 = x[:, 0::2, 1::2, :] # B H/2 W/2 C
- x3 = x[:, 1::2, 1::2, :] # B H/2 W/2 C
- x = torch.cat([x0, x1, x2, x3], -1) # B H/2 W/2 4*C
- x = x.view(B, -1, 4 * C) # B H/2*W/2 4*C
- x = self.norm(x)
- x = self.reduction(x)
- return x
- class BasicLayer(nn.Module):
- """ A basic Swin Transformer layer for one stage.
- Args:
- dim (int): Number of feature channels
- depth (int): Depths of this stage.
- num_heads (int): Number of attention head.
- window_size (int): Local window size. Default: 7.
- mlp_ratio (float): Ratio of mlp hidden dim to embedding dim. Default: 4.
- qkv_bias (bool, optional): If True, add a learnable bias to query, key, value. Default: True
- qk_scale (float | None, optional): Override default qk scale of head_dim ** -0.5 if set.
- drop (float, optional): Dropout rate. Default: 0.0
- attn_drop (float, optional): Attention dropout rate. Default: 0.0
- drop_path (float | tuple[float], optional): Stochastic depth rate. Default: 0.0
- norm_layer (nn.Module, optional): Normalization layer. Default: nn.LayerNorm
- downsample (nn.Module | None, optional): Downsample layer at the end of the layer. Default: None
- use_checkpoint (bool): Whether to use checkpointing to save memory. Default: False.
- """
- def __init__(self,
- dim,
- depth,
- num_heads,
- window_size=7,
- mlp_ratio=4.,
- qkv_bias=True,
- qk_scale=None,
- drop=0.,
- attn_drop=0.,
- drop_path=0.,
- norm_layer=nn.LayerNorm,
- downsample=None,
- use_checkpoint=False):
- super().__init__()
- self.window_size = window_size
- self.shift_size = window_size // 2
- self.depth = depth
- self.use_checkpoint = use_checkpoint
- # build blocks
- self.blocks = nn.ModuleList([
- SwinTransformerBlock(
- dim=dim,
- num_heads=num_heads,
- window_size=window_size,
- shift_size=0 if (i % 2 == 0) else window_size // 2,
- mlp_ratio=mlp_ratio,
- qkv_bias=qkv_bias,
- qk_scale=qk_scale,
- drop=drop,
- attn_drop=attn_drop,
- drop_path=drop_path[i] if isinstance(drop_path, list) else drop_path,
- norm_layer=norm_layer)
- for i in range(depth)])
- # patch merging layer
- if downsample is not None:
- self.downsample = downsample(dim=dim, norm_layer=norm_layer)
- else:
- self.downsample = None
- def forward(self, x, H, W):
- """ Forward function.
- Args:
- x: Input feature, tensor size (B, H*W, C).
- H, W: Spatial resolution of the input feature.
- """
- # calculate attention mask for SW-MSA
- Hp = int(np.ceil(H / self.window_size)) * self.window_size
- Wp = int(np.ceil(W / self.window_size)) * self.window_size
- img_mask = torch.zeros((1, Hp, Wp, 1), device=x.device) # 1 Hp Wp 1
- h_slices = (slice(0, -self.window_size),
- slice(-self.window_size, -self.shift_size),
- slice(-self.shift_size, None))
- w_slices = (slice(0, -self.window_size),
- slice(-self.window_size, -self.shift_size),
- slice(-self.shift_size, None))
- cnt = 0
- for h in h_slices:
- for w in w_slices:
- img_mask[:, h, w, :] = cnt
- cnt += 1
- mask_windows = window_partition(img_mask, self.window_size) # nW, window_size, window_size, 1
- mask_windows = mask_windows.view(-1, self.window_size * self.window_size)
- attn_mask = mask_windows.unsqueeze(1) - mask_windows.unsqueeze(2)
- attn_mask = attn_mask.masked_fill(attn_mask != 0, float(-100.0)).masked_fill(attn_mask == 0, float(0.0))
- for blk in self.blocks:
- blk.H, blk.W = H, W
- if self.use_checkpoint:
- x = checkpoint.checkpoint(blk, x, attn_mask)
- else:
- x = blk(x, attn_mask)
- if self.downsample is not None:
- x_down = self.downsample(x, H, W)
- Wh, Ww = (H + 1) // 2, (W + 1) // 2
- return x, H, W, x_down, Wh, Ww
- else:
- return x, H, W, x, H, W
- class PatchEmbed(nn.Module):
- """ Image to Patch Embedding
- Args:
- patch_size (int): Patch token size. Default: 4.
- in_chans (int): Number of input image channels. Default: 3.
- embed_dim (int): Number of linear projection output channels. Default: 96.
- norm_layer (nn.Module, optional): Normalization layer. Default: None
- """
- def __init__(self, patch_size=4, in_chans=3, embed_dim=96, norm_layer=None):
- super().__init__()
- patch_size = to_2tuple(patch_size)
- self.patch_size = patch_size
- self.in_chans = in_chans
- self.embed_dim = embed_dim
- self.proj = nn.Conv2d(in_chans, embed_dim, kernel_size=patch_size, stride=patch_size)
- if norm_layer is not None:
- self.norm = norm_layer(embed_dim)
- else:
- self.norm = None
- def forward(self, x):
- """Forward function."""
- # padding
- _, _, H, W = x.size()
- if W % self.patch_size[1] != 0:
- x = F.pad(x, (0, self.patch_size[1] - W % self.patch_size[1]))
- if H % self.patch_size[0] != 0:
- x = F.pad(x, (0, 0, 0, self.patch_size[0] - H % self.patch_size[0]))
- x = self.proj(x) # B C Wh Ww
- if self.norm is not None:
- Wh, Ww = x.size(2), x.size(3)
- x = x.flatten(2).transpose(1, 2)
- x = self.norm(x)
- x = x.transpose(1, 2).view(-1, self.embed_dim, Wh, Ww)
- return x
- class SwinTransformer(nn.Module):
- """ Swin Transformer backbone.
- A PyTorch impl of : `Swin Transformer: Hierarchical Vision Transformer using Shifted Windows` -
- https://arxiv.org/pdf/2103.14030
- Args:
- pretrain_img_size (int): Input image size for training the pretrained model,
- used in absolute postion embedding. Default 224.
- patch_size (int | tuple(int)): Patch size. Default: 4.
- in_chans (int): Number of input image channels. Default: 3.
- embed_dim (int): Number of linear projection output channels. Default: 96.
- depths (tuple[int]): Depths of each Swin Transformer stage.
- num_heads (tuple[int]): Number of attention head of each stage.
- window_size (int): Window size. Default: 7.
- mlp_ratio (float): Ratio of mlp hidden dim to embedding dim. Default: 4.
- qkv_bias (bool): If True, add a learnable bias to query, key, value. Default: True
- qk_scale (float): Override default qk scale of head_dim ** -0.5 if set.
- drop_rate (float): Dropout rate.
- attn_drop_rate (float): Attention dropout rate. Default: 0.
- drop_path_rate (float): Stochastic depth rate. Default: 0.2.
- norm_layer (nn.Module): Normalization layer. Default: nn.LayerNorm.
- ape (bool): If True, add absolute position embedding to the patch embedding. Default: False.
- patch_norm (bool): If True, add normalization after patch embedding. Default: True.
- out_indices (Sequence[int]): Output from which stages.
- frozen_stages (int): Stages to be frozen (stop grad and set eval mode).
- -1 means not freezing any parameters.
- use_checkpoint (bool): Whether to use checkpointing to save memory. Default: False.
- """
- def __init__(self,
- factor=0.5,
- depth_factor=0.5,
- pretrain_img_size=224,
- patch_size=4,
- in_chans=3,
- embed_dim=96,
- depths=[2, 2, 6, 2],
- num_heads=[3, 6, 12, 24],
- window_size=7,
- mlp_ratio=4.,
- qkv_bias=True,
- qk_scale=None,
- drop_rate=0.,
- attn_drop_rate=0.,
- drop_path_rate=0.2,
- norm_layer=nn.LayerNorm,
- ape=False,
- patch_norm=True,
- out_indices=(0, 1, 2, 3),
- frozen_stages=-1,
- use_checkpoint=False):
- super().__init__()
- embed_dim = int(embed_dim * factor)
- depths = [max(1, int(dim * depth_factor)) for dim in depths]
- self.pretrain_img_size = pretrain_img_size
- self.num_layers = len(depths)
- self.embed_dim = embed_dim
- self.ape = ape
- self.patch_norm = patch_norm
- self.out_indices = out_indices
- self.frozen_stages = frozen_stages
- # split image into non-overlapping patches
- self.patch_embed = PatchEmbed(
- patch_size=patch_size, in_chans=in_chans, embed_dim=embed_dim,
- norm_layer=norm_layer if self.patch_norm else None)
- # absolute position embedding
- if self.ape:
- pretrain_img_size = to_2tuple(pretrain_img_size)
- patch_size = to_2tuple(patch_size)
- patches_resolution = [pretrain_img_size[0] // patch_size[0], pretrain_img_size[1] // patch_size[1]]
- self.absolute_pos_embed = nn.Parameter(torch.zeros(1, embed_dim, patches_resolution[0], patches_resolution[1]))
- trunc_normal_(self.absolute_pos_embed, std=.02)
- self.pos_drop = nn.Dropout(p=drop_rate)
- # stochastic depth
- dpr = [x.item() for x in torch.linspace(0, drop_path_rate, sum(depths))] # stochastic depth decay rule
- # build layers
- self.layers = nn.ModuleList()
- for i_layer in range(self.num_layers):
- layer = BasicLayer(
- dim=int(embed_dim * 2 ** i_layer),
- depth=depths[i_layer],
- num_heads=num_heads[i_layer],
- window_size=window_size,
- mlp_ratio=mlp_ratio,
- qkv_bias=qkv_bias,
- qk_scale=qk_scale,
- drop=drop_rate,
- attn_drop=attn_drop_rate,
- drop_path=dpr[sum(depths[:i_layer]):sum(depths[:i_layer + 1])],
- norm_layer=norm_layer,
- downsample=PatchMerging if (i_layer < self.num_layers - 1) else None,
- use_checkpoint=use_checkpoint)
- self.layers.append(layer)
- num_features = [int(embed_dim * 2 ** i) for i in range(self.num_layers)]
- self.num_features = num_features
- # add a norm layer for each output
- for i_layer in out_indices:
- layer = norm_layer(num_features[i_layer])
- layer_name = f'norm{i_layer}'
- self.add_module(layer_name, layer)
- self.width_list = [i.size(1) for i in self.forward(torch.randn(1, 3, 640, 640))]
- def forward(self, x):
- """Forward function."""
- x = self.patch_embed(x)
- Wh, Ww = x.size(2), x.size(3)
- if self.ape:
- # interpolate the position embedding to the corresponding size
- absolute_pos_embed = F.interpolate(self.absolute_pos_embed, size=(Wh, Ww), mode='bicubic')
- x = (x + absolute_pos_embed).flatten(2).transpose(1, 2) # B Wh*Ww C
- else:
- x = x.flatten(2).transpose(1, 2)
- x = self.pos_drop(x)
- outs = []
- for i in range(self.num_layers):
- layer = self.layers[i]
- x_out, H, W, x, Wh, Ww = layer(x, Wh, Ww)
- if i in self.out_indices:
- norm_layer = getattr(self, f'norm{i}')
- x_out = norm_layer(x_out)
- out = x_out.view(-1, H, W, self.num_features[i]).permute(0, 3, 1, 2).contiguous()
- outs.append(out)
- return outs
4.1 修改一
第一还是建立文件,我们找到如下ultralytics/nn文件夹下建立一个目录名字呢就是'Addmodules'文件夹 (用群内的文件的话已经有了无需新建) !然后在其内部建立一个新的py文件将核心代码复制粘贴进去即可。

4.2 修改二
第二步我们在该目录下创建一个新的py文件名字为'__init__.py'( 用群内的文件的话已经有了无需新建) ,然后在其内部导入我们的检测头如下图所示。

4.3 修改三
第三步我门中到如下文件'ultralytics/nn/tasks.py'进行导入和注册我们的模块( 用群内的文件的话已经有了无需重新导入直接开始第四步即可) !
从今天开始以后的教程就都统一成这个样子了,因为我默认大家用了我群内的文件来进行修改!!

4.4 修改四
添加如下两行代码!!!

4.5 修改五
找到七百多行大概把具体看图片,按照图片来修改就行,添加红框内的部分,注意没有()只是 函数 名。

- elif m in {自行添加对应的模型即可,下面都是一样的}: # 这段代码是自己添加的原代码中没有
- m = m(*args)
- c2 = m.width_list # 返回通道列表
- backbone = True
4.6 修改六
下面的两个红框内都是需要改动的。

- if isinstance(c2, list):
- m_ = m
- m_.backbone = True
- else:
- m_ = nn.Sequential(*(m(*args) for _ in range(n))) if n > 1 else m(*args) # module
- t = str(m)[8:-2].replace('__main__.', '') # module type
- m.np = sum(x.numel() for x in m_.parameters()) # number params
- m_.i, m_.f, m_.type = i + 4 if backbone else i, f, t # attach index, 'from' index, type
4.7 修改七
如下的也需要修改,全部按照我的来。

代码如下把原先的代码替换了即可。
- if verbose:
- LOGGER.info(f'{i:>3}{str(f):>20}{n_:>3}{m.np:10.0f} {t:<45}{str(args):<30}') # print
- save.extend(x % (i + 4 if backbone else i) for x in ([f] if isinstance(f, int) else f) if x != -1) # append to savelist
- layers.append(m_)
- if i == 0:
- ch = []
- if isinstance(c2, list):
- ch.extend(c2)
- if len(c2) != 5:
- ch.insert(0, 0)
- else:
- ch.append(c2)
4.8 修改八
修改七和前面的都不太一样,需要修改前向传播中的一个部分, 已经离开了parse_model方法了。
可以在图片中开代码行数,没有离开task.py文件都是同一个文件。 同时这个部分有好几个前向传播都很相似,大家不要看错了, 是70多行左右的!!!,同时我后面提供了代码,大家直接复制粘贴即可,有时间我针对这里会出一个视频。

代码如下->
- def _predict_once(self, x, profile=False, visualize=False, embed=None):
- """
- Perform a forward pass through the network.
- Args:
- x (torch.Tensor): The input tensor to the model.
- profile (bool): Print the computation time of each layer if True, defaults to False.
- visualize (bool): Save the feature maps of the model if True, defaults to False.
- embed (list, optional): A list of feature vectors/embeddings to return.
- Returns:
- (torch.Tensor): The last output of the model.
- """
- y, dt, embeddings = [], [], [] # outputs
- for m in self.model:
- if m.f != -1: # if not from previous layer
- x = y[m.f] if isinstance(m.f, int) else [x if j == -1 else y[j] for j in m.f] # from earlier layers
- if profile:
- self._profile_one_layer(m, x, dt)
- if hasattr(m, 'backbone'):
- x = m(x)
- if len(x) != 5: # 0 - 5
- x.insert(0, None)
- for index, i in enumerate(x):
- if index in self.save:
- y.append(i)
- else:
- y.append(None)
- x = x[-1] # 最后一个输出传给下一层
- else:
- x = m(x) # run
- y.append(x if m.i in self.save else None) # save output
- if visualize:
- feature_visualization(x, m.type, m.i, save_dir=visualize)
- if embed and m.i in embed:
- embeddings.append(nn.functional.adaptive_avg_pool2d(x, (1, 1)).squeeze(-1).squeeze(-1)) # flatten
- if m.i == max(embed):
- return torch.unbind(torch.cat(embeddings, 1), dim=0)
- return x
到这里就完成了修改部分,但是这里面细节很多,大家千万要注意不要替换多余的代码,导致报错,也不要拉下任何一部,都会导致运行失败,而且报错很难排查!!!很难排查!!!
4.9 修改九
我们找到如下文件'ultralytics/utils/torch_utils.py'按照如下的图片进行修改,否则容易打印不出来计算量。

五、融合使用教程
训练信息:YOLO11-SwinTransformer-RepGFPN summary: 353 layers, 2,736,687 parameters, 2,736,671 gradients, 6.3 GFLOPs
- # Ultralytics YOLO 🚀, AGPL-3.0 license
- # YOLO11 object detection model with P3-P5 outputs. For Usage examples see https://docs.ultralytics.com/tasks/detect
- # Parameters
- nc: 80 # number of classes
- scales: # model compound scaling constants, i.e. 'model=yolo11n.yaml' will call yolo11.yaml with scale 'n'
- # [depth, width, max_channels]
- n: [0.50, 0.25, 1024] # summary: 319 layers, 2624080 parameters, 2624064 gradients, 6.6 GFLOPs
- s: [0.50, 0.50, 1024] # summary: 319 layers, 9458752 parameters, 9458736 gradients, 21.7 GFLOPs
- m: [0.50, 1.00, 512] # summary: 409 layers, 20114688 parameters, 20114672 gradients, 68.5 GFLOPs
- l: [1.00, 1.00, 512] # summary: 631 layers, 25372160 parameters, 25372144 gradients, 87.6 GFLOPs
- x: [1.00, 1.50, 512] # summary: 631 layers, 56966176 parameters, 56966160 gradients, 196.0 GFLOPs
- # 下面 [-1, 1, LSKNet, [0.25,0.5]] 参数位置的0.25是通道放缩的系数, YOLOv11N是0.25 YOLOv11S是0.5 YOLOv11M是1. YOLOv11l是1 YOLOv11是1.5大家根据自己训练的YOLO版本设定即可.
- # 0.5对应的是模型的深度系数
- # YOLO11n backbone
- backbone:
- # [from, repeats, module, args]
- - [-1, 1, SwinTransformer, [0.25,0.5]] # 0-4 P1/2
- # 0 1P2 2P3 3P4 4P5
- - [-1, 1, SPPF, [1024, 5]] # 5
- - [-1, 2, C2PSA, [1024]] # 6
- # YOLO11n head
- head:
- - [-1, 1, Conv, [512, 1, 1]] # 7
- - [3, 1, Conv, [512, 3, 2]]
- - [[-1, -2], 1, Concat, [1]]
- - [-1, 2, C3k2, [512, False]] # 10
- - [-1, 1, nn.Upsample, [None, 2, 'nearest']] #11
- - [2, 1, Conv, [256, 3, 2]] # 12
- - [[-2, -1, 3], 1, Concat, [1]]
- - [-1, 2, C3k2, [512, False]] # 14
- - [-1, 1, nn.Upsample, [None, 2, 'nearest']]
- - [[-1, 2], 1, Concat, [1]]
- - [-1, 2, C3k2, [256, False]] # 17
- - [-1, 1, Conv, [256, 3, 2]]
- - [[-1, 14], 1, Concat, [1]]
- - [-1, 2, C3k2, [512, False]] # 20
- - [14, 1, Conv, [256, 3, 2]] # 21
- - [20, 1, Conv, [256, 3, 2]] # 22
- - [[10, 21, -1], 1, Concat, [1]]
- - [-1, 2, C3k2, [1024, True]] # 24
- - [[17, 20, 24], 1, Detect, [nc]] # Detect(P3, P4, P5)
六、成功运行截图

七、本文总结
到此本文的正式分享内容就结束了,在这里给大家推荐我的YOLOv11改进有效涨点专栏,本专栏目前为新开的平均质量分97分,后期我会根据各种最新的前沿顶会进行论文复现,也会对一些老的改进机制进行补充,如果大家觉得本文帮助到你了,订阅本专栏,关注后续更多的更新~