一、本文介绍
本文给大家带来的改进机制是低照度 图像增强 网络 Retinexformer ,其是针对于黑夜 目标检测 的改进机制(非常适合大家用来发表论文),其主要思想是通过一种新颖的一阶段Retinex-based框架来增强低光图像。这个框架结合了照明信息的估计和损坏恢复,目的是提高低光图像的质量。核心在于照明引导的变换器,这种变换器使用照明信息来引导长期依赖性的建模,从而在不同照明条件下更好地处理图像。 欢迎大家订阅本专栏,本专栏每周更新3-5篇最新机制,更有包含我所有改进的文件和交流群提供给大家。
欢迎大家订阅我的专栏一起学习YOLO!
下图展示了Retinexformer相对于各种图像增强网络的对比效果 ,最新版本的Retinexformer在各种场景都表现的很优秀。

二、 Retinexformer的框架原理

官方论文地址: 官方论文地址点击即可跳转
官方代码地址: 官方代码地址点击即可跳转

Retinexformer的主要思想是通过一种新颖的一阶段Retinex-based框架来增强低光图像。这个框架结合了照明信息的估计和损坏恢复,目的是提高低光图像的质量。核心在于照明引导的 变换器 ,这种变换器使用照明信息来引导长期依赖性的建模,从而在不同照明条件下更好地处理图像。通过这种方式,Retinexformer能够有效地增强低光图像,同时保持图像的自然外观和细节。
其主要主要创新点如下:
1. 一阶段Retinex-based框架(ORF): 提出了一个简单但原则性的框架,用于估计照明信息以照亮低光图像,然后恢复损坏以产生增强图像。
2. 照明引导的变换器(IGT): 设计了一个照明引导变换器,利用照明表示来指导不同照明条件下区域的非局部相互作用建模。
3. 创新的自注意力机制(IG-MSA): 开发了一种新的自注意力机制,利用照明信息作为关键线索,指导长期依赖性的建模。
这些创新使Retinexformer在多个基准测试上显著优于现有的最先进方法,并在低光物体检测方面显示出其实际应用价值。

上图展示了Retinexformer方法的详细流程:
1. 输入图像与照明先验:
流程以一个低光照输入图像开始,通过某种方法得到照明先验
 。
。
2. 照明估计器:
它利用输入图像和照明先验来生成照明图
 ,该照明图用于指导后续图像的照亮过程。
,该照明图用于指导后续图像的照亮过程。
3. 照亮图像和特征提取:
照明图
 被用来照亮输入图像,生成照亮图像
被用来照亮输入图像,生成照亮图像
 ,同时会提取照亮特征
,同时会提取照亮特征
 。
。
4. 损坏恢复器—照明引导变换器: 包括多个照明引导的注意力块(IGAB),利用照亮特征来指导注意力机制,逐步恢复图像质量。
5. 照明引导的多头自注意力(IG-MSA): 这是IGAB的关键组成部分,通过照明信息引导自注意力计算,以捕获复杂的图像细节。
6. 最终图像输出: 通过层层处理,最终输出增强后的图像,这一图像在质量上有显著提升,色彩失真和噪声得到有效控制。
三、 Retinexformer的核心代码
代码的使用方式看章节四!
- import torch.nn as nn
- import torch
- import torch.nn.functional as F
- from einops import rearrange
- import math
- import warnings
- from torch.nn.init import _calculate_fan_in_and_fan_out
- __all__ = ['RetinexFormer']
- def _no_grad_trunc_normal_(tensor, mean, std, a, b):
- def norm_cdf(x):
- return (1. + math.erf(x / math.sqrt(2.))) / 2.
- if (mean < a - 2 * std) or (mean > b + 2 * std):
- warnings.warn("mean is more than 2 std from [a, b] in nn.init.trunc_normal_. "
- "The distribution of values may be incorrect.",
- stacklevel=2)
- with torch.no_grad():
- l = norm_cdf((a - mean) / std)
- u = norm_cdf((b - mean) / std)
- tensor.uniform_(2 * l - 1, 2 * u - 1)
- tensor.erfinv_()
- tensor.mul_(std * math.sqrt(2.))
- tensor.add_(mean)
- tensor.clamp_(min=a, max=b)
- return tensor
- def trunc_normal_(tensor, mean=0., std=1., a=-2., b=2.):
- # type: (Tensor, float, float, float, float) -> Tensor
- return _no_grad_trunc_normal_(tensor, mean, std, a, b)
- def variance_scaling_(tensor, scale=1.0, mode='fan_in', distribution='normal'):
- fan_in, fan_out = _calculate_fan_in_and_fan_out(tensor)
- if mode == 'fan_in':
- denom = fan_in
- elif mode == 'fan_out':
- denom = fan_out
- elif mode == 'fan_avg':
- denom = (fan_in + fan_out) / 2
- variance = scale / denom
- if distribution == "truncated_normal":
- trunc_normal_(tensor, std=math.sqrt(variance) / .87962566103423978)
- elif distribution == "normal":
- tensor.normal_(std=math.sqrt(variance))
- elif distribution == "uniform":
- bound = math.sqrt(3 * variance)
- tensor.uniform_(-bound, bound)
- else:
- raise ValueError(f"invalid distribution {distribution}")
- def lecun_normal_(tensor):
- variance_scaling_(tensor, mode='fan_in', distribution='truncated_normal')
- class PreNorm(nn.Module):
- def __init__(self, dim, fn):
- super().__init__()
- self.fn = fn
- self.norm = nn.LayerNorm(dim)
- def forward(self, x, *args, **kwargs):
- x = self.norm(x)
- return self.fn(x, *args, **kwargs)
- class GELU(nn.Module):
- def forward(self, x):
- return F.gelu(x)
- def conv(in_channels, out_channels, kernel_size, bias=False, padding=1, stride=1):
- return nn.Conv2d(
- in_channels, out_channels, kernel_size,
- padding=(kernel_size // 2), bias=bias, stride=stride)
- # input [bs,28,256,310] output [bs, 28, 256, 256]
- def shift_back(inputs, step=2):
- [bs, nC, row, col] = inputs.shape
- down_sample = 256 // row
- step = float(step) / float(down_sample * down_sample)
- out_col = row
- for i in range(nC):
- inputs[:, i, :, :out_col] = \
- inputs[:, i, :, int(step * i):int(step * i) + out_col]
- return inputs[:, :, :, :out_col]
- class Illumination_Estimator(nn.Module):
- def __init__(
- self, n_fea_middle, n_fea_in=4, n_fea_out=3): # __init__部分是内部属性,而forward的输入才是外部输入
- super(Illumination_Estimator, self).__init__()
- self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(n_fea_in, n_fea_middle, kernel_size=1, bias=True)
- self.depth_conv = nn.Conv2d(
- n_fea_middle, n_fea_middle, kernel_size=5, padding=2, bias=True, groups=n_fea_in)
- self.conv2 = nn.Conv2d(n_fea_middle, n_fea_out, kernel_size=1, bias=True)
- def forward(self, img):
- # img: b,c=3,h,w
- # mean_c: b,c=1,h,w
- # illu_fea: b,c,h,w
- # illu_map: b,c=3,h,w
- mean_c = img.mean(dim=1).unsqueeze(1)
- # stx()
- input = torch.cat([img, mean_c], dim=1)
- x_1 = self.conv1(input)
- illu_fea = self.depth_conv(x_1)
- illu_map = self.conv2(illu_fea)
- return illu_fea, illu_map
- class IG_MSA(nn.Module):
- def __init__(
- self,
- dim,
- dim_head=64,
- heads=8,
- ):
- super().__init__()
- self.num_heads = heads
- self.dim_head = dim_head
- self.to_q = nn.Linear(dim, dim_head * heads, bias=False)
- self.to_k = nn.Linear(dim, dim_head * heads, bias=False)
- self.to_v = nn.Linear(dim, dim_head * heads, bias=False)
- self.rescale = nn.Parameter(torch.ones(heads, 1, 1))
- self.proj = nn.Linear(dim_head * heads, dim, bias=True)
- self.pos_emb = nn.Sequential(
- nn.Conv2d(dim, dim, 3, 1, 1, bias=False, groups=dim),
- GELU(),
- nn.Conv2d(dim, dim, 3, 1, 1, bias=False, groups=dim),
- )
- self.dim = dim
- def forward(self, x_in, illu_fea_trans):
- """
- x_in: [b,h,w,c] # input_feature
- illu_fea: [b,h,w,c] # mask shift? 为什么是 b, h, w, c?
- return out: [b,h,w,c]
- """
- b, h, w, c = x_in.shape
- x = x_in.reshape(b, h * w, c)
- q_inp = self.to_q(x)
- k_inp = self.to_k(x)
- v_inp = self.to_v(x)
- illu_attn = illu_fea_trans # illu_fea: b,c,h,w -> b,h,w,c
- q, k, v, illu_attn = map(lambda t: rearrange(t, 'b n (h d) -> b h n d', h=self.num_heads),
- (q_inp, k_inp, v_inp, illu_attn.flatten(1, 2)))
- v = v * illu_attn
- # q: b,heads,hw,c
- q = q.transpose(-2, -1)
- k = k.transpose(-2, -1)
- v = v.transpose(-2, -1)
- q = F.normalize(q, dim=-1, p=2)
- k = F.normalize(k, dim=-1, p=2)
- attn = (k @ q.transpose(-2, -1)) # A = K^T*Q
- attn = attn * self.rescale
- attn = attn.softmax(dim=-1)
- x = attn @ v # b,heads,d,hw
- x = x.permute(0, 3, 1, 2) # Transpose
- x = x.reshape(b, h * w, self.num_heads * self.dim_head)
- out_c = self.proj(x).view(b, h, w, c)
- out_p = self.pos_emb(v_inp.reshape(b, h, w, c).permute(
- 0, 3, 1, 2)).permute(0, 2, 3, 1)
- out = out_c + out_p
- return out
- class FeedForward(nn.Module):
- def __init__(self, dim, mult=4):
- super().__init__()
- self.net = nn.Sequential(
- nn.Conv2d(dim, dim * mult, 1, 1, bias=False),
- GELU(),
- nn.Conv2d(dim * mult, dim * mult, 3, 1, 1,
- bias=False, groups=dim * mult),
- GELU(),
- nn.Conv2d(dim * mult, dim, 1, 1, bias=False),
- )
- def forward(self, x):
- """
- x: [b,h,w,c]
- return out: [b,h,w,c]
- """
- out = self.net(x.permute(0, 3, 1, 2))
- return out.permute(0, 2, 3, 1)
- class IGAB(nn.Module):
- def __init__(
- self,
- dim,
- dim_head=64,
- heads=8,
- num_blocks=2,
- ):
- super().__init__()
- self.blocks = nn.ModuleList([])
- for _ in range(num_blocks):
- self.blocks.append(nn.ModuleList([
- IG_MSA(dim=dim, dim_head=dim_head, heads=heads),
- PreNorm(dim, FeedForward(dim=dim))
- ]))
- def forward(self, x, illu_fea):
- """
- x: [b,c,h,w]
- illu_fea: [b,c,h,w]
- return out: [b,c,h,w]
- """
- x = x.permute(0, 2, 3, 1)
- for (attn, ff) in self.blocks:
- x = attn(x, illu_fea_trans=illu_fea.permute(0, 2, 3, 1)) + x
- x = ff(x) + x
- out = x.permute(0, 3, 1, 2)
- return out
- class Denoiser(nn.Module):
- def __init__(self, in_dim=3, out_dim=3, dim=31, level=2, num_blocks=[2, 4, 4]):
- super(Denoiser, self).__init__()
- self.dim = dim
- self.level = level
- # Input projection
- self.embedding = nn.Conv2d(in_dim, self.dim, 3, 1, 1, bias=False)
- # Encoder
- self.encoder_layers = nn.ModuleList([])
- dim_level = dim
- for i in range(level):
- self.encoder_layers.append(nn.ModuleList([
- IGAB(
- dim=dim_level, num_blocks=num_blocks[i], dim_head=dim, heads=dim_level // dim),
- nn.Conv2d(dim_level, dim_level * 2, 4, 2, 1, bias=False),
- nn.Conv2d(dim_level, dim_level * 2, 4, 2, 1, bias=False)
- ]))
- dim_level *= 2
- # Bottleneck
- self.bottleneck = IGAB(
- dim=dim_level, dim_head=dim, heads=dim_level // dim, num_blocks=num_blocks[-1])
- # Decoder
- self.decoder_layers = nn.ModuleList([])
- for i in range(level):
- self.decoder_layers.append(nn.ModuleList([
- nn.ConvTranspose2d(dim_level, dim_level // 2, stride=2,
- kernel_size=2, padding=0, output_padding=0),
- nn.Conv2d(dim_level, dim_level // 2, 1, 1, bias=False),
- IGAB(
- dim=dim_level // 2, num_blocks=num_blocks[level - 1 - i], dim_head=dim,
- heads=(dim_level // 2) // dim),
- ]))
- dim_level //= 2
- # Output projection
- self.mapping = nn.Conv2d(self.dim, out_dim, 3, 1, 1, bias=False)
- # activation function
- self.lrelu = nn.LeakyReLU(negative_slope=0.1, inplace=True)
- self.apply(self._init_weights)
- def _init_weights(self, m):
- if isinstance(m, nn.Linear):
- trunc_normal_(m.weight, std=.02)
- if isinstance(m, nn.Linear) and m.bias is not None:
- nn.init.constant_(m.bias, 0)
- elif isinstance(m, nn.LayerNorm):
- nn.init.constant_(m.bias, 0)
- nn.init.constant_(m.weight, 1.0)
- def forward(self, x, illu_fea):
- """
- x: [b,c,h,w] x是feature, 不是image
- illu_fea: [b,c,h,w]
- return out: [b,c,h,w]
- """
- # Embedding
- fea = self.embedding(x)
- # Encoder
- fea_encoder = []
- illu_fea_list = []
- for (IGAB, FeaDownSample, IlluFeaDownsample) in self.encoder_layers:
- fea = IGAB(fea, illu_fea) # bchw
- illu_fea_list.append(illu_fea)
- fea_encoder.append(fea)
- fea = FeaDownSample(fea)
- illu_fea = IlluFeaDownsample(illu_fea)
- # Bottleneck
- fea = self.bottleneck(fea, illu_fea)
- # Decoder
- for i, (FeaUpSample, Fution, LeWinBlcok) in enumerate(self.decoder_layers):
- fea = FeaUpSample(fea)
- fea = Fution(
- torch.cat([fea, fea_encoder[self.level - 1 - i]], dim=1))
- illu_fea = illu_fea_list[self.level - 1 - i]
- fea = LeWinBlcok(fea, illu_fea)
- # Mapping
- out = self.mapping(fea) + x
- return out
- class RetinexFormer_Single_Stage(nn.Module):
- def __init__(self, in_channels=3, out_channels=3, n_feat=31, level=2, num_blocks=[1, 1, 1]):
- super(RetinexFormer_Single_Stage, self).__init__()
- self.estimator = Illumination_Estimator(n_feat)
- self.denoiser = Denoiser(in_dim=in_channels, out_dim=out_channels, dim=n_feat, level=level,
- num_blocks=num_blocks) #### 将 Denoiser 改为 img2img
- def forward(self, img):
- # img: b,c=3,h,w
- # illu_fea: b,c,h,w
- # illu_map: b,c=3,h,w
- illu_fea, illu_map = self.estimator(img)
- input_img = img * illu_map + img
- output_img = self.denoiser(input_img, illu_fea)
- return output_img
- class RetinexFormer(nn.Module):
- def __init__(self, in_channels=3, out_channels=3, n_feat=8, stage=1, num_blocks=[1,2,2]):
- super(RetinexFormer, self).__init__()
- self.stage = stage
- modules_body = [
- RetinexFormer_Single_Stage(in_channels=in_channels, out_channels=out_channels, n_feat=n_feat, level=2,
- num_blocks=num_blocks)
- for _ in range(stage)]
- self.body = nn.Sequential(*modules_body)
- def forward(self, x):
- """
- x: [b,c,h,w]
- return out:[b,c,h,w]
- """
- out = self.body(x)
- return out
- if __name__ == '__main__':
- # from fvcore.nn import FlopCountAnalysis
- model = RetinexFormer(stage=1,n_feat=40,num_blocks=[1,2,2]).cuda()
- inputs = torch.randn((1, 3, 256, 256)).cuda()
- out = model(inputs)
- print(out.size())
四、 Retinexformer 的添加方式
这个添加方式和之前的变了一下,以后的添加方法都按照这个来了,是为了和群内的文件适配。
4.1 修改一
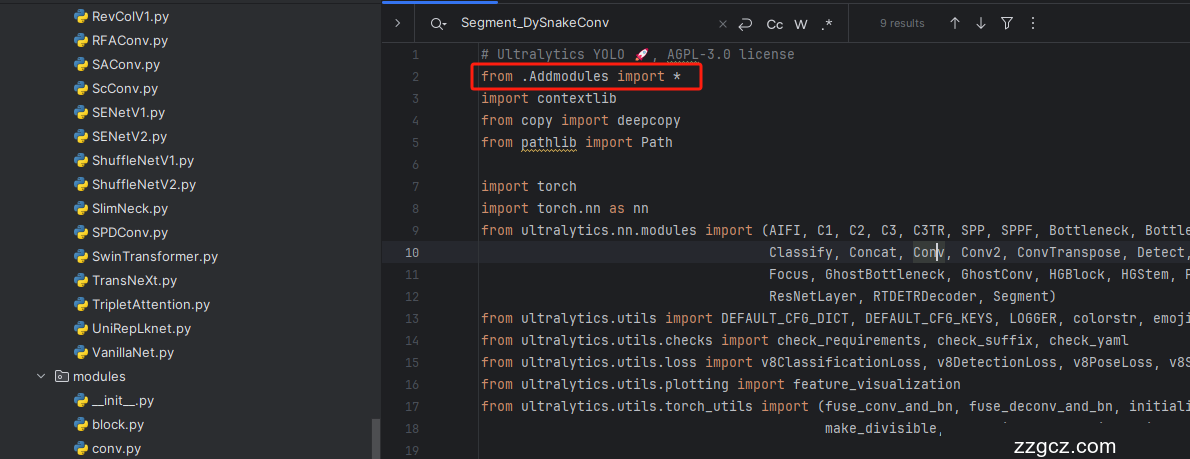
第一还是建立文件,我们找到如下 ultralytics /nn/modules文件夹下建立一个目录名字呢就是'Addmodules'文件夹( 用群内的文件的话已经有了无需新建) !然后在其内部建立一个新的py文件将核心代码复制粘贴进去即可。

4.2 修改二
第二步我们在该目录下创建一个新的py文件名字为'__init__.py'( 用群内的文件的话已经有了无需新建) ,然后在其内部导入我们的检测头如下图所示。

4.3 修改三
第三步我门中到如下文件'ultralytics/nn/tasks.py'进行导入和注册我们的模块( 用群内的文件的话已经有了无需重新导入直接开始第四步即可) !
从今天开始以后的教程就都统一成这个样子了,因为我默认大家用了我群内的文件来进行修改!!
4.4 修改四
按照我的添加在parse_model里添加即可。

到此就完事了注册的工作,该模型无需添加任何参数是一种无参的机制,所以导入进来即可。
关闭混合精度验证!
找到'ultralytics/engine/validator.py'文件找到 'class BaseValidator:' 然后在其'__call__'中 self.args.half = self.device.type != 'cpu' # force FP16 val during training的一行代码下面加上self.args.half = False
打印计算量的问题!
计算的GFLOPs计算 异常 不打印,所以需要额外修改一处, 我们找到如下文件'ultralytics/utils/torch_utils.py'文件内有如下的代码按照如下的图片进行修改,大家看好函数就行,其中红框的640可能和你的不一样, 然后用我给的代码替换掉整个代码即可。

- def get_flops(model, imgsz=640):
- """Return a YOLO model's FLOPs."""
- try:
- model = de_parallel(model)
- p = next(model.parameters())
- # stride = max(int(model.stride.max()), 32) if hasattr(model, 'stride') else 32 # max stride
- stride = 640
- im = torch.empty((1, 3, stride, stride), device=p.device) # input image in BCHW format
- flops = thop.profile(deepcopy(model), inputs=[im], verbose=False)[0] / 1E9 * 2 if thop else 0 # stride GFLOPs
- imgsz = imgsz if isinstance(imgsz, list) else [imgsz, imgsz] # expand if int/float
- return flops * imgsz[0] / stride * imgsz[1] / stride # 640x640 GFLOPs
- except Exception:
- return 0
五、 Retinexformer 的yaml文件和运行记录
5.1 Retinexformer 的yaml文件
训练信息:YOLO11-Retinexformer summary: 385 layers, 2,624,436 parameters, 2,624,420 gradients, 34.4 GFLOPs
- # Ultralytics YOLO 🚀, AGPL-3.0 license
- # YOLO11 object detection model with P3-P5 outputs. For Usage examples see https://docs.ultralytics.com/tasks/detect
- # Parameters
- nc: 80 # number of classes
- scales: # model compound scaling constants, i.e. 'model=yolo11n.yaml' will call yolo11.yaml with scale 'n'
- # [depth, width, max_channels]
- n: [0.50, 0.25, 1024] # summary: 319 layers, 2624080 parameters, 2624064 gradients, 6.6 GFLOPs
- s: [0.50, 0.50, 1024] # summary: 319 layers, 9458752 parameters, 9458736 gradients, 21.7 GFLOPs
- m: [0.50, 1.00, 512] # summary: 409 layers, 20114688 parameters, 20114672 gradients, 68.5 GFLOPs
- l: [1.00, 1.00, 512] # summary: 631 layers, 25372160 parameters, 25372144 gradients, 87.6 GFLOPs
- x: [1.00, 1.50, 512] # summary: 631 layers, 56966176 parameters, 56966160 gradients, 196.0 GFLOPs
- # YOLO11n backbone
- backbone:
- # [from, repeats, module, args]
- - [-1, 1, RetinexFormer, []] # 0-P1/2
- - [-1, 1, Conv, [64, 3, 2]] # 1-P1/2
- - [-1, 1, Conv, [128, 3, 2]] # 2-P2/4
- - [-1, 2, C3k2, [256, False, 0.25]]
- - [-1, 1, Conv, [256, 3, 2]] # 4-P3/8
- - [-1, 2, C3k2, [512, False, 0.25]]
- - [-1, 1, Conv, [512, 3, 2]] # 6-P4/16
- - [-1, 2, C3k2, [512, True]]
- - [-1, 1, Conv, [1024, 3, 2]] # 8-P5/32
- - [-1, 2, C3k2, [1024, True]]
- - [-1, 1, SPPF, [1024, 5]] # 10
- - [-1, 2, C2PSA, [1024]] # 11
- # YOLO11n head
- head:
- - [-1, 1, nn.Upsample, [None, 2, "nearest"]]
- - [[-1, 7], 1, Concat, [1]] # cat backbone P4
- - [-1, 2, C3k2, [512, False]] # 14
- - [-1, 1, nn.Upsample, [None, 2, "nearest"]]
- - [[-1, 5], 1, Concat, [1]] # cat backbone P3
- - [-1, 2, C3k2, [256, False]] # 17 (P3/8-small)
- - [-1, 1, Conv, [256, 3, 2]]
- - [[-1, 14], 1, Concat, [1]] # cat head P4
- - [-1, 2, C3k2, [512, False]] # 20 (P4/16-medium)
- - [-1, 1, Conv, [512, 3, 2]]
- - [[-1, 11], 1, Concat, [1]] # cat head P5
- - [-1, 2, C3k2, [1024, True]] # 23 (P5/32-large)
- - [[17, 20, 23], 1, Detect, [nc]] # Detect(P3, P4, P5)
5.2 Retinexformer 的训练过程截图

五、本文总结
到此本文的正式分享内容就结束了,在这里给大家推荐我的YOLOv11改进有效涨点专栏,本专栏目前为新开的平均质量分98分,后期我会根据各种最新的前沿顶会进行论文复现,也会对一些老的改进机制进行补充,如果大家觉得本文帮助到你了,订阅本专栏,关注后续更多的更新~