💡💡💡本文独家改进:新颖的下采样ADown来自于YOLOv9,助力YOLOv8,将ADown添加在backbone和head处,提供多个yaml改进方法
💡💡💡在多个私有数据集和公开数据集VisDrone2019、PASCAL VOC实现涨点
收录
YOLOv8原创自研
💡💡💡全网独家首发创新(原创),适合paper !!!
💡💡💡 2024年计算机视觉顶会创新点适用于Yolov5、Yolov7、Yolov8等各个Yolo系列,专栏文章提供每一步步骤和源码,轻松带你上手魔改网络 !!!
💡💡💡重点:通过本专栏的阅读,后续你也可以设计魔改网络,在网络不同位置(Backbone、head、detect、loss等)进行魔改,实现创新!!!
1.YOLOv9原理介绍

论文: 2402.13616.pdf (arxiv.org)
代码:GitHub - WongKinYiu/yolov9: Implementation of paper - YOLOv9: Learning What You Want to Learn Using Programmable Gradient Information摘要: 如今的深度学习方法重点关注如何设计最合适的目标函数,从而使得模型的预测结果能够最接近真实情况。同时,必须设计一个适当的架构,可以帮助获取足够的信息进行预测。然而,现有方法忽略了一个事实,即当输入数据经过逐层特征提取和空间变换时,大量信息将会丢失。因此,YOLOv9 深入研究了数据通过深度网络传输时数据丢失的重要问题,即信息瓶颈和可逆函数。作者提出了可编程梯度信息(programmable gradient information,PGI)的概念,来应对深度网络实现多个目标所需要的各种变化。PGI 可以为目标任务计算目标函数提供完整的输入信息,从而获得可靠的梯度信息来更新网络权值。此外,研究者基于梯度路径规划设计了一种新的轻量级网络架构,即通用高效层聚合网络(Generalized Efficient Layer Aggregation Network,GELAN)。该架构证实了 PGI 可以在轻量级模型上取得优异的结果。研究者在基于 MS COCO 数据集的目标检测任务上验证所提出的 GELAN 和 PGI。结果表明,与其他 SOTA 方法相比,GELAN 仅使用传统卷积算子即可实现更好的参数利用率。对于 PGI 而言,它的适用性很强,可用于从轻型到大型的各种模型。我们可以用它来获取完整的信息,从而使从头开始训练的模型能够比使用大型数据集预训练的 SOTA 模型获得更好的结果。对比结果如图1所示。

YOLOv9架构图(来自集智书童)

可编程梯度信息(PGI):使用PGI改善训练过程
旨在解决深度网络中的信息瓶颈问题的策略
1)主分支:用于推理,无需额外的推理成本。
2)辅助可逆分支:解决网络加深带来的问题,如信息瓶颈,以生成可靠梯度。
3)多级辅助信息:解决深度监督导致的错误累积问题,特别适用于具有多个预测分支的架构和轻量模型。
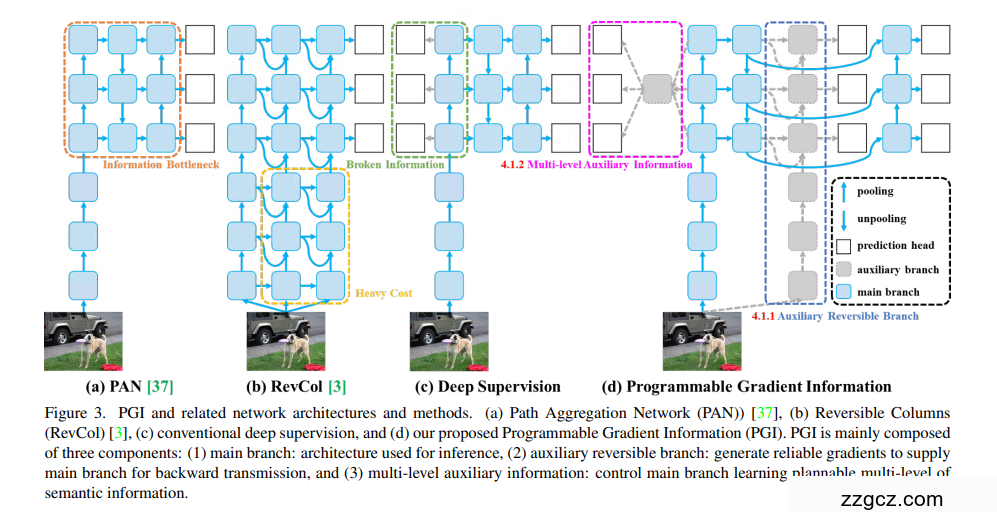
广义高效层聚合网络(GELAN):使用GELAN改进架构
GELAN通过结合两种神经网络架构,即结合用梯度路径规划(CSPNet)和(ELAN)设计了一种广义的高效层聚合网络(GELAN);GELAN综合考虑了轻量级、推理速度和准确度。
特征1:综合设计 - GELAN融合了CSPNet和ELAN的设计理念,创建了一个灵活的网络架构,能够根据不同的应用需求和计算资源进行调整。
CSPNet通过分割和合并特征图来减少冗余计算,而ELAN则使用层聚合来增强特征的表示能力。
特征2:计算块的自由选择 - 与传统的深度网络架构依赖特定类型的计算单元不同,GELAN允许在其框架内使用各种类型的计算块,比如传统的卷积层、深度可分卷积或者其他类型的新颖计算单元。

2.ADown如何将入到YOLOv8
2.1 新建py文件 ultralytics/nn/yolov9.py
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.nn.functional as F
import numpy as np
from ultralytics.nn.modules.conv import Conv,autopad
class RepConvN(nn.Module):
"""RepConv is a basic rep-style block, including training and deploy status
This code is based on https://github.com/DingXiaoH/RepVGG/blob/main/repvgg.py
"""
default_act = nn.SiLU() # default activation
def __init__(self, c1, c2, k=3, s=1, p=1, g=1, d=1, act=True, bn=False, deploy=False):
super().__init__()
assert k == 3 and p == 1
self.g = g
self.c1 = c1
self.c2 = c2
self.act = self.default_act if act is True else act if isinstance(act, nn.Module) else nn.Identity()
self.bn = None
self.conv1 = Conv(c1, c2, k, s, p=p, g=g, act=False)
self.conv2 = Conv(c1, c2, 1, s, p=(p - k // 2), g=g, act=False)
def forward_fuse(self, x):
"""Forward process"""
return self.act(self.conv(x))
def forward(self, x):
"""Forward process"""
if hasattr(self, 'conv'):
return self.forward_fuse(x)
id_out = 0 if self.bn is None else self.bn(x)
return self.act(self.conv1(x) + self.conv2(x) + id_out)
def get_equivalent_kernel_bias(self):
kernel3x3, bias3x3 = self._fuse_bn_tensor(self.conv1)
kernel1x1, bias1x1 = self._fuse_bn_tensor(self.conv2)
kernelid, biasid = self._fuse_bn_tensor(self.bn)
return kernel3x3 + self._pad_1x1_to_3x3_tensor(kernel1x1) + kernelid, bias3x3 + bias1x1 + biasid
def _avg_to_3x3_tensor(self, avgp):
channels = self.c1
groups = self.g
kernel_size = avgp.kernel_size
input_dim = channels // groups
k = torch.zeros((channels, input_dim, kernel_size, kernel_size))
k[np.arange(channels), np.tile(np.arange(input_dim), groups), :, :] = 1.0 / kernel_size ** 2
return k
def _pad_1x1_to_3x3_tensor(self, kernel1x1):
if kernel1x1 is None:
return 0
else:
return torch.nn.functional.pad(kernel1x1, [1, 1, 1, 1])
def _fuse_bn_tensor(self, branch):
if branch is None:
return 0, 0
if isinstance(branch, Conv):
kernel = branch.conv.weight
running_mean = branch.bn.running_mean
running_var = branch.bn.running_var
gamma = branch.bn.weight
beta = branch.bn.bias
eps = branch.bn.eps
elif isinstance(branch, nn.BatchNorm2d):
if not hasattr(self, 'id_tensor'):
input_dim = self.c1 // self.g
kernel_value = np.zeros((self.c1, input_dim, 3, 3), dtype=np.float32)
for i in range(self.c1):
kernel_value[i, i % input_dim, 1, 1] = 1
self.id_tensor = torch.from_numpy(kernel_value).to(branch.weight.device)
kernel = self.id_tensor
running_mean = branch.running_mean
running_var = branch.running_var
gamma = branch.weight
beta = branch.bias
eps = branch.eps
std = (running_var + eps).sqrt()
t = (gamma / std).reshape(-1, 1, 1, 1)
return kernel * t, beta - running_mean * gamma / std
def switch_to_deploy(self):
if hasattr(self, 'conv'):
return
kernel, bias = self.get_equivalent_kernel_bias()
self.conv = nn.Conv2d(in_channels=self.conv1.conv.in_channels,
out_channels=self.conv1.conv.out_channels,
kernel_size=self.conv1.conv.kernel_size,
stride=self.conv1.conv.stride,
padding=self.conv1.conv.padding,
dilation=self.conv1.conv.dilation,
groups=self.conv1.conv.groups,
bias=True).requires_grad_(False)
self.conv.weight.data = kernel
self.conv.bias.data = bias
for para in self.parameters():
para.detach_()
self.__delattr__('conv1')
self.__delattr__('conv2')
if hasattr(self, 'nm'):
self.__delattr__('nm')
if hasattr(self, 'bn'):
self.__delattr__('bn')
if hasattr(self, 'id_tensor'):
self.__delattr__('id_tensor')
class RepNBottleneck(nn.Module):
# Standard bottleneck
def __init__(self, c1, c2, shortcut=True, g=1, k=(3, 3), e=0.5): # ch_in, ch_out, shortcut, kernels, groups, expand
super().__init__()
c_ = int(c2 * e) # hidden channels
self.cv1 = RepConvN(c1, c_, k[0], 1)
self.cv2 = Conv(c_, c2, k[1], 1, g=g)
self.add = shortcut and c1 == c2
def forward(self, x):
return x + self.cv2(self.cv1(x)) if self.add else self.cv2(self.cv1(x))
class RepNCSP(nn.Module):
# CSP Bottleneck with 3 convolutions
def __init__(self, c1, c2, n=1, shortcut=True, g=1, e=0.5): # ch_in, ch_out, number, shortcut, groups, expansion
super().__init__()
c_ = int(c2 * e) # hidden channels
self.cv1 = Conv(c1, c_, 1, 1)
self.cv2 = Conv(c1, c_, 1, 1)
self.cv3 = Conv(2 * c_, c2, 1) # optional act=FReLU(c2)
self.m = nn.Sequential(*(RepNBottleneck(c_, c_, shortcut, g, e=1.0) for _ in range(n)))
def forward(self, x):
return self.cv3(torch.cat((self.m(self.cv1(x)), self.cv2(x)), 1))
class RepNCSPELAN4(nn.Module):
# csp-elan
def __init__(self, c1, c2, c3, c4, c5=1): # ch_in, ch_out, number, shortcut, groups, expansion
super().__init__()
self.c = c3//2
self.cv1 = Conv(c1, c3, 1, 1)
self.cv2 = nn.Sequential(RepNCSP(c3//2, c4, c5), Conv(c4, c4, 3, 1))
self.cv3 = nn.Sequential(RepNCSP(c4, c4, c5), Conv(c4, c4, 3, 1))
self.cv4 = Conv(c3+(2*c4), c2, 1, 1)
def forward(self, x):
y = list(self.cv1(x).chunk(2, 1))
y.extend((m(y[-1])) for m in [self.cv2, self.cv3])
return self.cv4(torch.cat(y, 1))
def forward_split(self, x):
y = list(self.cv1(x).split((self.c, self.c), 1))
y.extend(m(y[-1]) for m in [self.cv2, self.cv3])
return self.cv4(torch.cat(y, 1))
class ADown(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, c1, c2): # ch_in, ch_out, shortcut, kernels, groups, expand
super().__init__()
self.c = c2 // 2
self.cv1 = Conv(c1 // 2, self.c, 3, 2, 1)
self.cv2 = Conv(c1 // 2, self.c, 1, 1, 0)
def forward(self, x):
x = torch.nn.functional.avg_pool2d(x, 2, 1, 0, False, True)
x1,x2 = x.chunk(2, 1)
x1 = self.cv1(x1)
x2 = torch.nn.functional.max_pool2d(x2, 3, 2, 1)
x2 = self.cv2(x2)
return torch.cat((x1, x2), 1)
class CBLinear(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, c1, c2s, k=1, s=1, p=None, g=1): # ch_in, ch_outs, kernel, stride, padding, groups
super(CBLinear, self).__init__()
self.c2s = c2s
self.conv = nn.Conv2d(c1, sum(c2s), k, s, autopad(k, p), groups=g, bias=True)
def forward(self, x):
outs = self.conv(x).split(self.c2s, dim=1)
return outs
class CBFuse(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, idx):
super(CBFuse, self).__init__()
self.idx = idx
def forward(self, xs):
target_size = xs[-1].shape[2:]
res = [F.interpolate(x[self.idx[i]], size=target_size, mode='nearest') for i, x in enumerate(xs[:-1])]
out = torch.sum(torch.stack(res + xs[-1:]), dim=0)
return out
class Silence(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(Silence, self).__init__()
def forward(self, x):
return x2.2 注册ultralytics/nn/tasks.py
1)首先ADown进行注册
from ultralytics.nn.yolov9 import ADown2)修改 def parse_model(d, ch, verbose=True): # model_dict, input_channels(3)
if m in (
Classify,
Conv,
ConvTranspose,
GhostConv,
Bottleneck,
GhostBottleneck,
SPP,
SPPF,
DWConv,
Focus,
BottleneckCSP,
C1,
C2,
C2f,
C2fAttn,
C3,
C3TR,
C3Ghost,
nn.ConvTranspose2d,
DWConvTranspose2d,
C3x,
RepC3,
ADown
):2.3 yolov8-ADown.yaml
# Ultralytics YOLO 🚀, AGPL-3.0 license
# YOLOv8 object detection model with P3-P5 outputs. For Usage examples see https://docs.ultralytics.com/tasks/detect
# Parameters
nc: 80 # number of classes
scales: # model compound scaling constants, i.e. 'model=yolov8n.yaml' will call yolov8.yaml with scale 'n'
# [depth, width, max_channels]
n: [0.33, 0.25, 1024] # YOLOv8n summary: 225 layers, 3157200 parameters, 3157184 gradients, 8.9 GFLOPs
s: [0.33, 0.50, 1024] # YOLOv8s summary: 225 layers, 11166560 parameters, 11166544 gradients, 28.8 GFLOPs
m: [0.67, 0.75, 768] # YOLOv8m summary: 295 layers, 25902640 parameters, 25902624 gradients, 79.3 GFLOPs
l: [1.00, 1.00, 512] # YOLOv8l summary: 365 layers, 43691520 parameters, 43691504 gradients, 165.7 GFLOPs
x: [1.00, 1.25, 512] # YOLOv8x summary: 365 layers, 68229648 parameters, 68229632 gradients, 258.5 GFLOPs
# YOLOv8.0n backbone
backbone:
# [from, repeats, module, args]
- [-1, 1, Conv, [64, 3, 2]] # 0-P1/2
- [-1, 1, Conv, [128, 3, 2]] # 1-P2/4
- [-1, 3, C2f, [128, True]]
- [-1, 1, ADown, [256]] # 3-P3/8
- [-1, 6, C2f, [256, True]]
- [-1, 1, ADown, [512]] # 5-P4/16
- [-1, 6, C2f, [512, True]]
- [-1, 1, ADown, [1024]] # 7-P5/32
- [-1, 3, C2f, [1024, True]]
- [-1, 1, SPPF, [1024, 5]] # 9
# YOLOv8.0n head
head:
- [-1, 1, nn.Upsample, [None, 2, 'nearest']]
- [[-1, 6], 1, Concat, [1]] # cat backbone P4
- [-1, 3, C2f, [512]] # 12
- [-1, 1, nn.Upsample, [None, 2, 'nearest']]
- [[-1, 4], 1, Concat, [1]] # cat backbone P3
- [-1, 3, C2f, [256]] # 15 (P3/8-small)
- [-1, 1, ADown, [256]]
- [[-1, 12], 1, Concat, [1]] # cat head P4
- [-1, 3, C2f, [512]] # 18 (P4/16-medium)
- [-1, 1, ADown, [512]]
- [[-1, 9], 1, Concat, [1]] # cat head P5
- [-1, 3, C2f, [1024]] # 21 (P5/32-large)
- [[15, 18, 21], 1, Detect, [nc]] # Detect(P3, P4, P5)
2.4 yolov8-ADown-backbone.yaml
# Ultralytics YOLO 🚀, AGPL-3.0 license
# YOLOv8 object detection model with P3-P5 outputs. For Usage examples see https://docs.ultralytics.com/tasks/detect
# Parameters
nc: 80 # number of classes
scales: # model compound scaling constants, i.e. 'model=yolov8n.yaml' will call yolov8.yaml with scale 'n'
# [depth, width, max_channels]
n: [0.33, 0.25, 1024] # YOLOv8n summary: 225 layers, 3157200 parameters, 3157184 gradients, 8.9 GFLOPs
s: [0.33, 0.50, 1024] # YOLOv8s summary: 225 layers, 11166560 parameters, 11166544 gradients, 28.8 GFLOPs
m: [0.67, 0.75, 768] # YOLOv8m summary: 295 layers, 25902640 parameters, 25902624 gradients, 79.3 GFLOPs
l: [1.00, 1.00, 512] # YOLOv8l summary: 365 layers, 43691520 parameters, 43691504 gradients, 165.7 GFLOPs
x: [1.00, 1.25, 512] # YOLOv8x summary: 365 layers, 68229648 parameters, 68229632 gradients, 258.5 GFLOPs
# YOLOv8.0n backbone
backbone:
# [from, repeats, module, args]
- [-1, 1, Conv, [64, 3, 2]] # 0-P1/2
- [-1, 1, Conv, [128, 3, 2]] # 1-P2/4
- [-1, 3, C2f, [128, True]]
- [-1, 1, ADown, [256]] # 3-P3/8
- [-1, 6, C2f, [256, True]]
- [-1, 1, ADown, [512]] # 5-P4/16
- [-1, 6, C2f, [512, True]]
- [-1, 1, ADown, [1024]] # 7-P5/32
- [-1, 3, C2f, [1024, True]]
- [-1, 1, SPPF, [1024, 5]] # 9
# YOLOv8.0n head
head:
- [-1, 1, nn.Upsample, [None, 2, "nearest"]]
- [[-1, 6], 1, Concat, [1]] # cat backbone P4
- [-1, 3, C2f, [512]] # 12
- [-1, 1, nn.Upsample, [None, 2, "nearest"]]
- [[-1, 4], 1, Concat, [1]] # cat backbone P3
- [-1, 3, C2f, [256]] # 15 (P3/8-small)
- [-1, 1, Conv, [256, 3, 2]]
- [[-1, 12], 1, Concat, [1]] # cat head P4
- [-1, 3, C2f, [512]] # 18 (P4/16-medium)
- [-1, 1, Conv, [512, 3, 2]]
- [[-1, 9], 1, Concat, [1]] # cat head P5
- [-1, 3, C2f, [1024]] # 21 (P5/32-large)
- [[15, 18, 21], 1, Detect, [nc]] # Detect(P3, P4, P5)