💡💡💡本文独家改进:CVPR2024 TransXNet 聚合注意力增强版AggregatedAttention加入到YOLOv8以及巧妙的和C2f结合。
改进结构图如下:
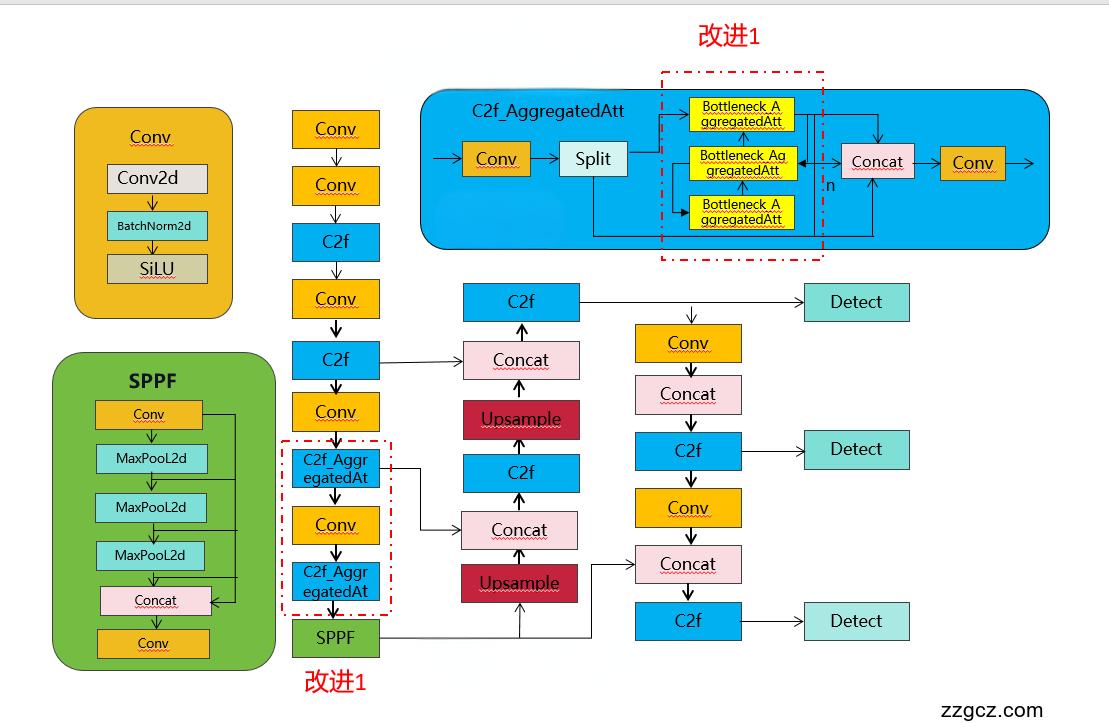
收录
YOLOv8原创自研
💡💡💡全网独家首发创新(原创),适合paper !!!
💡💡💡 2024年计算机视觉顶会创新点适用于Yolov5、Yolov7、Yolov8等各个Yolo系列,专栏文章提供每一步步骤和源码,轻松带你上手魔改网络 !!!
💡💡💡重点:通过本专栏的阅读,后续你也可以设计魔改网络,在网络不同位置(Backbone、head、detect、loss等)进行魔改,实现创新!!!
1.TransXNet原理介绍
问题点:
本文依旧从经典的 ViTs 说起,即基于 MHSA 构建远距离建模实现全局感受野的覆盖,但缺乏像 CNNs 般的归纳偏差能力。因此在泛化能力上相对较弱,需要大量的训练样本和数据增强策略来弥补。
本文:为了解决上述问题,这篇论文针对性地引入了一种新的混合网络模块,称为Dual Dynamic Token Mixer (D-Mixer),它以一种依赖于输入的方式聚合全局信息和局部细节。具体来说,输入特征被分成两部分,分别经过一个全局自注意力模块和一个依赖于输入的深度卷积模块进行处理,然后将两个输出连接在一起。这种简单的设计可以使网络同时看到全局和局部信息,从而增强了归纳偏差。论文中的实验证明,这种方法在感受野方面表现出色,即网络可以看到更广泛的上下文信息。

提出了一个轻量级的双动态token混频器(D-Mixer),它以一种依赖输入的方式聚合全局信息和局部细节。D-Mixer的工作原理是在均匀分割的特征段上分别应用高效的全局注意模块和输入依赖的深度卷积,从而赋予网络强大的归纳偏置和扩大的有效接受野。用D-Mixer作为基本构建块来设计TransXNet,这是一种新颖的混合CNN-Transformer视觉骨干网络。

如图1所示,提出的TransXNet采用了四个阶段的分层架构。每个阶段由一个patch嵌入层和几个顺序堆叠的块组成。使用7×7卷积层(步幅=4)实现第一个patch嵌入层,然后使用批归一化(BN),而其余阶段的patch嵌入层使用3×3卷积层(步幅=2)和BN。每个块由一个动态位置编码(DPE)层、一个双动态token混频器(D-Mixer)和一个多尺度前馈网络(MS-FFN)组成。

Overlapping Spatial Reduction Attention (OSRA)
空间降维注意(SRA)在前人的研究中得到了广泛的应用,利用稀疏标记区域关系高效提取全局信息。然而,为了减少标记计数而进行的非重叠空间缩减打破了patch边界附近的空间结构,降低了token的质量。为了解决这一问题,在SRA中引入了重叠空间缩减(OSR),通过使用更大的重叠斑块来更好地表示斑块边界附近的空间结构。在实践中,将OSR实例化为深度可分离卷积,其中步幅跟随PVT,内核大小等于步幅加3。

作者设计了一种像素聚焦注意力机制,它在每个Query附近具有细粒度的感知,同时同时保持全局信息的粗粒度意识。为了实现眼球运动中固有的像素级平移等价性,作者采用了一种双路径设计,包括以Query为中心的滑动窗口注意力和池化注意力。

理论部分详见:
TransNeXt:昨日最强模型已不强,TransNeXt-Tiny在ImageNet上准确率刷到84.0% - 知乎 (zhihu.com)
2. TransXNet加入YOLOv8
2.1 新建ultralytics/nn/backbone/TransNeXt/transnextblcok.py
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.nn.functional as F
import numpy as np
from functools import partial
from timm.models.layers import DropPath, to_2tuple, trunc_normal_
import math
import swattention
from ultralytics.nn.modules.conv import Conv,autopad
from ultralytics.nn.modules.block import C3,C2f,Bottleneck
CUDA_NUM_THREADS = 128
class sw_av_cuda(torch.autograd.Function):
@staticmethod
def forward(ctx, attn_weight, value, height, width, kernel_size):
output = swattention.av_forward(attn_weight, value, height, width, kernel_size, CUDA_NUM_THREADS)
ctx.save_for_backward(attn_weight, value)
ctx.height, ctx.width, ctx.kernel_size = height, width, kernel_size
return output
@staticmethod
def backward(ctx, d_output):
attn_weight, value = ctx.saved_tensors
height, width, kernel_size = ctx.height, ctx.width, ctx.kernel_size
d_attn_weight, d_value = swattention.av_backward(d_output.contiguous(), attn_weight, value, height, width,
kernel_size, CUDA_NUM_THREADS)
return d_attn_weight, d_value, None, None, None
class sw_qkrpb_cuda(torch.autograd.Function):
@staticmethod
def forward(ctx, query, key, rpb, height, width, kernel_size):
attn_weight = swattention.qk_rpb_forward(query, key, rpb, height, width, kernel_size, CUDA_NUM_THREADS)
ctx.save_for_backward(query, key)
ctx.height, ctx.width, ctx.kernel_size = height, width, kernel_size
return attn_weight
@staticmethod
def backward(ctx, d_attn_weight):
query, key = ctx.saved_tensors
height, width, kernel_size = ctx.height, ctx.width, ctx.kernel_size
d_query, d_key, d_rpb = swattention.qk_rpb_backward(d_attn_weight.contiguous(), query, key, height, width,
kernel_size, CUDA_NUM_THREADS)
return d_query, d_key, d_rpb, None, None, None
@torch.no_grad()
def get_seqlen_scale(input_resolution, window_size):
return torch.nn.functional.avg_pool2d(torch.ones(1, input_resolution[0], input_resolution[1]) * (window_size ** 2),
window_size, stride=1, padding=window_size // 2, ).reshape(-1, 1)
@torch.no_grad()
def get_relative_position_cpb(query_size, key_size, pretrain_size=None):
# device = torch.device('cuda' if torch.cuda.is_available() else 'cpu')
pretrain_size = pretrain_size or query_size
axis_qh = torch.arange(query_size[0], dtype=torch.float32)
axis_kh = F.adaptive_avg_pool1d(axis_qh.unsqueeze(0), key_size[0]).squeeze(0)
axis_qw = torch.arange(query_size[1], dtype=torch.float32)
axis_kw = F.adaptive_avg_pool1d(axis_qw.unsqueeze(0), key_size[1]).squeeze(0)
axis_kh, axis_kw = torch.meshgrid(axis_kh, axis_kw)
axis_qh, axis_qw = torch.meshgrid(axis_qh, axis_qw)
axis_kh = torch.reshape(axis_kh, [-1])
axis_kw = torch.reshape(axis_kw, [-1])
axis_qh = torch.reshape(axis_qh, [-1])
axis_qw = torch.reshape(axis_qw, [-1])
relative_h = (axis_qh[:, None] - axis_kh[None, :]) / (pretrain_size[0] - 1) * 8
relative_w = (axis_qw[:, None] - axis_kw[None, :]) / (pretrain_size[1] - 1) * 8
relative_hw = torch.stack([relative_h, relative_w], dim=-1).view(-1, 2)
relative_coords_table, idx_map = torch.unique(relative_hw, return_inverse=True, dim=0)
relative_coords_table = torch.sign(relative_coords_table) * torch.log2(
torch.abs(relative_coords_table) + 1.0) / torch.log2(torch.tensor(8, dtype=torch.float32))
return idx_map, relative_coords_table
class AggregatedAttention(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, dim, input_resolution, num_heads=8, window_size=3, qkv_bias=True,
attn_drop=0., proj_drop=0., sr_ratio=1):
super().__init__()
assert dim % num_heads == 0, f"dim {dim} should be divided by num_heads {num_heads}."
self.dim = dim
self.num_heads = num_heads
self.head_dim = dim // num_heads
self.sr_ratio = sr_ratio
assert window_size % 2 == 1, "window size must be odd"
self.window_size = window_size
self.local_len = window_size ** 2
self.pool_H, self.pool_W = input_resolution[0] // self.sr_ratio, input_resolution[1] // self.sr_ratio
self.pool_len = self.pool_H * self.pool_W
self.unfold = nn.Unfold(kernel_size=window_size, padding=window_size // 2, stride=1)
self.temperature = nn.Parameter(
torch.log((torch.ones(num_heads, 1, 1) / 0.24).exp() - 1)) # Initialize softplus(temperature) to 1/0.24.
self.q = nn.Linear(dim, dim, bias=qkv_bias)
self.query_embedding = nn.Parameter(
nn.init.trunc_normal_(torch.empty(self.num_heads, 1, self.head_dim), mean=0, std=0.02))
self.kv = nn.Linear(dim, dim * 2, bias=qkv_bias)
self.attn_drop = nn.Dropout(attn_drop)
self.proj = nn.Linear(dim, dim)
self.proj_drop = nn.Dropout(proj_drop)
# Components to generate pooled features.
self.pool = nn.AdaptiveAvgPool2d((self.pool_H, self.pool_W))
self.sr = nn.Conv2d(dim, dim, kernel_size=1, stride=1, padding=0)
self.norm = nn.LayerNorm(dim)
self.act = nn.GELU()
# mlp to generate continuous relative position bias
self.cpb_fc1 = nn.Linear(2, 512, bias=True)
self.cpb_act = nn.ReLU(inplace=True)
self.cpb_fc2 = nn.Linear(512, num_heads, bias=True)
# relative bias for local features
self.relative_pos_bias_local = nn.Parameter(
nn.init.trunc_normal_(torch.empty(num_heads, self.local_len), mean=0, std=0.0004))
# Generate padding_mask && sequnce length scale
local_seq_length = get_seqlen_scale(input_resolution, window_size)
self.register_buffer("seq_length_scale", torch.as_tensor(np.log(local_seq_length.numpy() + self.pool_len)),
persistent=False)
# dynamic_local_bias:
self.learnable_tokens = nn.Parameter(
nn.init.trunc_normal_(torch.empty(num_heads, self.head_dim, self.local_len), mean=0, std=0.02))
self.learnable_bias = nn.Parameter(torch.zeros(num_heads, 1, self.local_len))
def forward(self, x, H, W, relative_pos_index, relative_coords_table):
B, N, C = x.shape
# Generate queries, normalize them with L2, add query embedding, and then magnify with sequence length scale and temperature.
# Use softplus function ensuring that the temperature is not lower than 0.
q_norm = F.normalize(self.q(x).reshape(B, N, self.num_heads, self.head_dim).permute(0, 2, 1, 3), dim=-1)
q_norm_scaled = (q_norm + self.query_embedding) * F.softplus(self.temperature) * self.seq_length_scale
# Generate unfolded keys and values and l2-normalize them
k_local, v_local = self.kv(x).reshape(B, N, 2 * self.num_heads, self.head_dim).permute(0, 2, 1, 3).chunk(2,
dim=1)
# Compute local similarity
attn_local = sw_qkrpb_cuda.apply(q_norm_scaled.contiguous(), F.normalize(k_local, dim=-1).contiguous(),
self.relative_pos_bias_local,
H, W, self.window_size)
# Generate pooled features
x_ = x.permute(0, 2, 1).reshape(B, -1, H, W).contiguous()
x_ = self.pool(self.act(self.sr(x_))).reshape(B, -1, self.pool_len).permute(0, 2, 1)
x_ = self.norm(x_)
# Generate pooled keys and values
kv_pool = self.kv(x_).reshape(B, self.pool_len, 2 * self.num_heads, self.head_dim).permute(0, 2, 1, 3)
k_pool, v_pool = kv_pool.chunk(2, dim=1)
# Use MLP to generate continuous relative positional bias for pooled features.
pool_bias = self.cpb_fc2(self.cpb_act(self.cpb_fc1(relative_coords_table))).transpose(0, 1)[:,
relative_pos_index.view(-1)].view(-1, N, self.pool_len)
# Compute pooled similarity
attn_pool = q_norm_scaled @ F.normalize(k_pool, dim=-1).transpose(-2, -1) + pool_bias
# Concatenate local & pooled similarity matrices and calculate attention weights through the same Softmax
attn = torch.cat([attn_local, attn_pool], dim=-1).softmax(dim=-1)
attn = self.attn_drop(attn)
# Split the attention weights and separately aggregate the values of local & pooled features
attn_local, attn_pool = torch.split(attn, [self.local_len, self.pool_len], dim=-1)
attn_local = (q_norm @ self.learnable_tokens) + self.learnable_bias + attn_local
x_local = sw_av_cuda.apply(attn_local.type_as(v_local), v_local.contiguous(), H, W, self.window_size)
x_pool = attn_pool @ v_pool
x = (x_local + x_pool).transpose(1, 2).reshape(B, N, C)
# Linear projection and output
x = self.proj(x)
x = self.proj_drop(x)
return x
class transnext_AggregatedAttention(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, dim, input_resolution, sr_ratio=8, num_heads=8, window_size=3, qkv_bias=True,
attn_drop=0., proj_drop=0.) -> None:
super().__init__()
if type(input_resolution) == int:
input_resolution = (input_resolution, input_resolution)
relative_pos_index, relative_coords_table = get_relative_position_cpb(
query_size=input_resolution,
key_size=(20, 20),
pretrain_size=input_resolution)
self.register_buffer(f"relative_pos_index", relative_pos_index, persistent=False)
self.register_buffer(f"relative_coords_table", relative_coords_table, persistent=False)
self.attention = AggregatedAttention(dim, input_resolution, num_heads, window_size, qkv_bias, attn_drop, proj_drop, sr_ratio)
def forward(self, x):
B, _, H, W = x.size()
x = x.flatten(2).transpose(1, 2)
relative_pos_index = getattr(self, f"relative_pos_index")
relative_coords_table = getattr(self, f"relative_coords_table")
x = self.attention(x, H, W, relative_pos_index.to(x.device), relative_coords_table.to(x.device))
x = x.reshape(B, H, W, -1).permute(0, 3, 1, 2).contiguous()
return x
class Bottleneck_AggregatedAttention(Bottleneck):
"""Standard bottleneck With CloAttention."""
def __init__(self, c1, c2, input_resolution, sr_ratio, shortcut=True, g=1, k=..., e=0.5):
super().__init__(c1, c2, shortcut, g, k, e)
self.attention = transnext_AggregatedAttention(c2, input_resolution, sr_ratio)
def forward(self, x):
"""'forward()' applies the YOLOv5 FPN to input data."""
return x + self.attention(self.cv2(self.cv1(x))) if self.add else self.attention(self.cv2(self.cv1(x)))
class C2f_AggregatedAttention(C2f):
def __init__(self, c1, c2, n=1, input_resolution=None, sr_ratio=None, shortcut=False, g=1, e=0.5):
super().__init__(c1, c2, n, shortcut, g, e)
self.m = nn.ModuleList(
Bottleneck_AggregatedAttention(self.c, self.c, input_resolution, sr_ratio, shortcut, g, k=(3, 3), e=1.0) for
_ in range(n))
class C3_AggregatedAttention(C3):
def __init__(self, c1, c2, n=1, input_resolution=None, sr_ratio=None, shortcut=False, g=1, e=0.5):
super().__init__(c1, c2, n, shortcut, g, e)
c_ = int(c2 * e) # hidden channels
self.m = nn.Sequential(
*(Bottleneck_AggregatedAttention(c_, c_, input_resolution, sr_ratio, shortcut, g, k=((1, 1), (3, 3)), e=1.0)
for _ in range(n)))2.2修改task.py
1)首先进行注册
from ultralytics.nn.backbone.TransNeXt.transnextblcok import *2)修改def parse_model(d, ch, verbose=True): # model_dict, input_channels(3)
只需要在你源码基础上加入C2f_AggregatedAttention,其他模块为博主其他文章的优化点
n = n_ = max(round(n * depth), 1) if n > 1 else n # depth gain
if m in (
Classify,
Conv,
ConvTranspose,
GhostConv,
Bottleneck,
GhostBottleneck,
SPP,
SPPF,
DWConv,
Focus,
BottleneckCSP,
C1,
C2,
C2f,
C2fAttn,
C3,
C3TR,
C3Ghost,
nn.ConvTranspose2d,
DWConvTranspose2d,
C3x,
RepC3,
transnext_AggregatedAttention,C2f_AggregatedAttention
):
c1, c2 = ch[f], args[0]
if c2 != nc: # if c2 not equal to number of classes (i.e. for Classify() output)
c2 = make_divisible(min(c2, max_channels) * width, 8)
args = [c1, c2, *args[1:]]
if m in (BottleneckCSP, C1, C2, C2f, C2fAttn, C3, C3TR, C3Ghost, C3x, RepC3,C2f_AggregatedAttention):
args.insert(2, n) # number of repeats
n = 12.3 yolov8-C2f_AggregatedAtt.yaml

# Ultralytics YOLO 🚀, AGPL-3.0 license
# YOLOv8 object detection model with P3-P5 outputs. For Usage examples see https://docs.ultralytics.com/tasks/detect
# Parameters
nc: 80 # number of classes
scales: # model compound scaling constants, i.e. 'model=yolov8n.yaml' will call yolov8.yaml with scale 'n'
# [depth, width, max_channels]
n: [0.33, 0.25, 1024] # YOLOv8n summary: 225 layers, 3157200 parameters, 3157184 gradients, 8.9 GFLOPs
s: [0.33, 0.50, 1024] # YOLOv8s summary: 225 layers, 11166560 parameters, 11166544 gradients, 28.8 GFLOPs
m: [0.67, 0.75, 768] # YOLOv8m summary: 295 layers, 25902640 parameters, 25902624 gradients, 79.3 GFLOPs
l: [1.00, 1.00, 512] # YOLOv8l summary: 365 layers, 43691520 parameters, 43691504 gradients, 165.7 GFLOPs
x: [1.00, 1.25, 512] # YOLOv8x summary: 365 layers, 68229648 parameters, 68229632 gradients, 258.5 GFLOPs
# YOLOv8.0n backbone
backbone:
# [from, repeats, module, args]
- [-1, 1, Conv, [64, 3, 2]] # 0-P1/2
- [-1, 1, Conv, [128, 3, 2]] # 1-P2/4
- [-1, 3, C2f, [128, True]]
- [-1, 1, Conv, [256, 3, 2]] # 3-P3/8
- [-1, 6, C2f, [256, True]]
- [-1, 1, Conv, [512, 3, 2]] # 5-P4/16
- [-1, 6, C2f_AggregatedAttention, [512, 40, 2, True]]
- [-1, 1, Conv, [1024, 3, 2]] # 7-P5/32
- [-1, 3, C2f_AggregatedAttention, [1024, 20, 1, True]]
- [-1, 1, SPPF, [1024, 5]] # 9
# YOLOv8.0n head
head:
- [-1, 1, nn.Upsample, [None, 2, 'nearest']]
- [[-1, 6], 1, Concat, [1]] # cat backbone P4
- [-1, 3, C2f, [512]] # 12
- [-1, 1, nn.Upsample, [None, 2, 'nearest']]
- [[-1, 4], 1, Concat, [1]] # cat backbone P3
- [-1, 3, C2f, [256]] # 15 (P3/8-small)
- [-1, 1, Conv, [256, 3, 2]]
- [[-1, 12], 1, Concat, [1]] # cat head P4
- [-1, 3, C2f, [512]] # 18 (P4/16-medium)
- [-1, 1, Conv, [512, 3, 2]]
- [[-1, 9], 1, Concat, [1]] # cat head P5
- [-1, 3, C2f, [1024]] # 21 (P5/32-large)
- [[15, 18, 21], 1, Detect, [nc]] # Detect(P3, P4, P5)
2.4 报错解决
q_norm_scaled = (q_norm + self.query_embedding) * F.softplus(self.temperature) * self.seq_length_scale
RuntimeError: The size of tensor a (256) must match the size of tensor b (1600) at non-singleton dimension 2修改class DetectionModel(BaseModel):
替换为如下:
# Build strides
m = self.model[-1] # Detect()
if isinstance(m, Detect): # includes all Detect subclasses like Segment, Pose, OBB, WorldDetect
s = 640 # 2x min stride
m.inplace = self.inplace
forward = lambda x: self.forward(x)[0] if isinstance(m, (Segment, Pose, OBB)) else self.forward(x)
"""
m.stride = torch.tensor([s / x.shape[-2] for x in forward(torch.zeros(1, ch, s, s))]) # forward
self.model.to(torch.device('cuda'))
self.stride = m.stride
m.bias_init() # only run once
"""
try:
m.stride = torch.tensor([s / x.shape[-2] for x in forward(torch.zeros(2, ch, s, s))]) # forward
except RuntimeError as e:
if 'Not implemented on the CPU' in str(e) or 'Input type (torch.FloatTensor) and weight type (torch.cuda.FloatTensor)' in str(e) or 'CUDA tensor' in str(e) or 'is_cuda()' in str(e):
self.model.to(torch.device('cuda'))
m.stride = torch.tensor([s / x.shape[-2] for x in forward(torch.zeros(2, ch, s, s).to(torch.device('cuda')))]) # forward
else:
raise e
self.stride = m.stride
m.bias_init() # only run once2.5 swattention编译
源码下载:https://github.com/DaiShiResearch/TransNeXt

cd swattention_extension
pip install . 编译成功
 论文:
论文: