💡💡💡问题点:大规模视觉预训练显著提高了大型视觉模型的性能,即现有的低FLOPs模型不能从大规模的预训练中获益
💡💡💡解决对策:ParameterNet,旨在增加大规模视觉预训练模型中的参数数量,同时最小化FLOPs的增加,利用动态卷积将额外的参数合并到网络中。
💡💡💡动态卷积引入到YOLOv8:1) DynamicConv;2)DynamicConv+Bn+Act;
使用方法:直接代替YOLOv8中的卷积;
💡💡💡在多个数据集上涨点的前提下,降低GFLOPs,具体实验性能如下表
| parameters | GFLOPs | |
| yolov8s | 11166560 | 28.8 |
| yolov8s-DynamicConv | 17996813 | 24.9 |
| yolov8s-DynamicBnAct | 17999373 | 24.9 |
| yolov8n | 3011823 | 8.2 |
| yolov8n-DynamicConv | 4727293 | 7.3 |
| yolov8n-DynamicBnAct | 4728573 | 7.3 |
改进结构图:
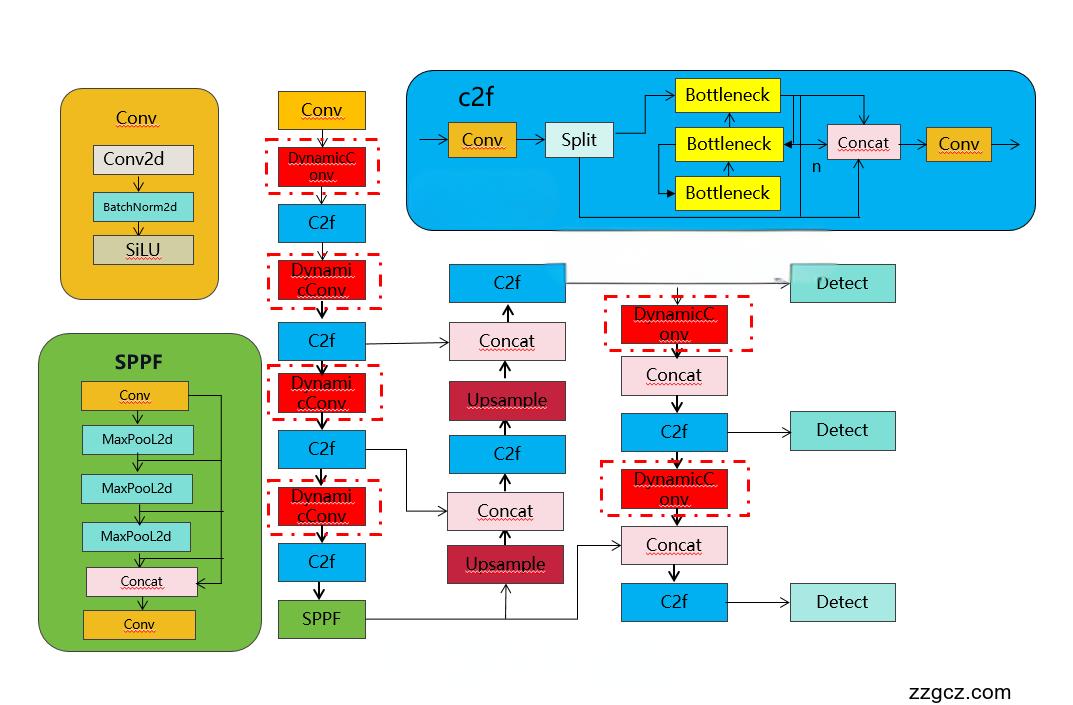
收录
YOLOv8原创自研
💡💡💡全网独家首发创新(原创),适合paper !!!
💡💡💡 2024年计算机视觉顶会创新点适用于Yolov5、Yolov7、Yolov8等各个Yolo系列,专栏文章提供每一步步骤和源码,轻松带你上手魔改网络 !!!
💡💡💡重点:通过本专栏的阅读,后续你也可以设计魔改网络,在网络不同位置(Backbone、head、detect、loss等)进行魔改,实现创新!!!
1.原理介绍

论文: https://arxiv.org/pdf/2306.14525v2.pdf
摘要:大规模视觉预训练显著提高了大型视觉模型的性能。然而,我们观察到低FLOPs的缺陷,即现有的低FLOPs模型不能从大规模的预训练中获益。在本文中,我们引入了一种新的设计原则,称为ParameterNet,旨在增加大规模视觉预训练模型中的参数数量,同时最小化FLOPs的增加。我们利用动态卷积将额外的参数合并到网络中,而FLOPs仅略有上升。ParameterNet方法允许低flops网络利用大规模视觉预训练。此外,我们将参数网的概念扩展到语言领域,在保持推理速度的同时增强推理结果。在大规模ImageNet-22K上的实验证明了该方案的优越性。例如ParameterNet-600M可以在ImageNet上实现比广泛使用的Swin Transformer更高的精度(81.6%对80.9%),并且具有更低的FLOPs (0.6G对4.5G)。在语言领域,使用ParameterNet增强的LLaMA- 1b比普通LLaMA准确率提高了2%

参数数量和FLOPs之间存在高度的相关性。具有大量参数的模型通常拥有较高的FLOPs。考虑到大量数据需要更多的参数的直觉,作者通过增加参数数量来构建ParameterNet,同时保持低FLOPs。

主要考虑高效的动态卷积,它可以多倍增加参数的数量,几乎不带来额外的 FLOPs。


2.DynamicConv引入YOLOv8
2.1 新建MLCA加入ultralytics/nn/block/parameternet.py
import math
from functools import partial
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.nn.functional as F
from timm.layers import drop_path
from timm.models.layers import SelectAdaptivePool2d, Linear, CondConv2d, hard_sigmoid, make_divisible, DropPath
from ultralytics.nn.modules.conv import Conv, autopad
from ultralytics.nn.modules.block import Bottleneck,C2f
class DynamicConv_Single(nn.Module):
""" Dynamic Conv layer
"""
def __init__(self, in_features, out_features, kernel_size=1, stride=1, padding='', dilation=1,
groups=1, bias=False, num_experts=4):
super().__init__()
self.routing = nn.Linear(in_features, num_experts)
self.cond_conv = CondConv2d(in_features, out_features, kernel_size, stride, padding, dilation,
groups, bias, num_experts)
def forward(self, x):
pooled_inputs = F.adaptive_avg_pool2d(x, 1).flatten(1) # CondConv routing
routing_weights = torch.sigmoid(self.routing(pooled_inputs))
x = self.cond_conv(x, routing_weights)
return x
class DynamicConv(nn.Module):
default_act = nn.SiLU() # default activation
def __init__(self, c1, c2, k=1, s=1, p=None, g=1, d=1, act=True, num_experts=4):
super().__init__()
self.conv = nn.Sequential(
DynamicConv_Single(c1, c2, kernel_size=k, stride=s, padding=autopad(k, p, d), dilation=d, groups=g, num_experts=num_experts),
nn.BatchNorm2d(c2),
self.default_act if act is True else act if isinstance(act, nn.Module) else nn.Identity()
)
def forward(self, x):
return self.conv(x)
class DynamicBnAct(nn.Module):
""" Conv + Norm Layer + Activation w/ optional skip connection
"""
def __init__(
self, in_chs, out_chs, kernel_size, stride=1, dilation=1, pad_type=None,
skip=False, act_layer=nn.ReLU, norm_layer=nn.BatchNorm2d, drop_path_rate=0., num_experts=4):
super(DynamicBnAct, self).__init__()
self.has_residual = skip and stride == 1 and in_chs == out_chs
self.drop_path_rate = drop_path_rate
# self.conv = create_conv2d(in_chs, out_chs, kernel_size, stride=stride, dilation=dilation, padding=pad_type)
self.conv = DynamicConv(in_chs, out_chs, kernel_size, stride,p=pad_type, d=dilation , num_experts=num_experts)
self.bn1 = norm_layer(out_chs)
self.act1 = act_layer()
def feature_info(self, location):
if location == 'expansion': # output of conv after act, same as block coutput
info = dict(module='act1', hook_type='forward', num_chs=self.conv.out_channels)
else: # location == 'bottleneck', block output
info = dict(module='', hook_type='', num_chs=self.conv.out_channels)
return info
def forward(self, x):
shortcut = x
x = self.conv(x)
x = self.bn1(x)
x = self.act1(x)
if self.has_residual:
if self.drop_path_rate > 0.:
x = drop_path(x, self.drop_path_rate, self.training)
x += shortcut
return x
2.2 注册ultralytics/nn/tasks.py
1)第一处修改:
DynamicConv,DynamicBnAct进行注册
from ultralytics.nn.block.parameternet import DynamicConv,DynamicBnAct2)第二处修改:
修改def parse_model(d, ch, verbose=True): # model_dict, input_channels(3)
只需要在你源码基础上加入DynamicConv,DynamicBnAct
if m in (Classify, Conv, ConvTranspose, GhostConv, Bottleneck, GhostBottleneck, SPP, SPPF, DWConv, Focus,
BottleneckCSP, C1, C2, C2f, C3, C3TR, C3Ghost, nn.ConvTranspose2d, DWConvTranspose2d, C3x, RepC3,DynamicConv,DynamicBnAct):
c1, c2 = ch[f], args[0]
if c2 != nc: # if c2 not equal to number of classes (i.e. for Classify() output)
c2 = make_divisible(min(c2, max_channels) * width, 8)
args = [c1, c2, *args[1:]]
if m in (BottleneckCSP, C1, C2, C2f, C3, C3TR, C3Ghost, C3x, RepC3):
args.insert(2, n) # number of repeats
n = 12.3 yolov8_DynamicConv.yaml

# Ultralytics YOLO 🚀, AGPL-3.0 license
# YOLOv8 object detection model with P3-P5 outputs. For Usage examples see https://docs.ultralytics.com/tasks/detect
# Parameters
nc: 80 # number of classes
scales: # model compound scaling constants, i.e. 'model=yolov8n.yaml' will call yolov8.yaml with scale 'n'
# [depth, width, max_channels]
n: [0.33, 0.25, 1024] # YOLOv8n summary: 225 layers, 3157200 parameters, 3157184 gradients, 8.9 GFLOPs
s: [0.33, 0.50, 1024] # YOLOv8s summary: 225 layers, 11166560 parameters, 11166544 gradients, 28.8 GFLOPs
m: [0.67, 0.75, 768] # YOLOv8m summary: 295 layers, 25902640 parameters, 25902624 gradients, 79.3 GFLOPs
l: [1.00, 1.00, 512] # YOLOv8l summary: 365 layers, 43691520 parameters, 43691504 gradients, 165.7 GFLOPs
x: [1.00, 1.25, 512] # YOLOv8x summary: 365 layers, 68229648 parameters, 68229632 gradients, 258.5 GFLOPs
# YOLOv8.0n backbone
backbone:
# [from, repeats, module, args]
- [-1, 1, Conv, [64, 3, 2]] # 0-P1/2
- [-1, 1, Conv, [128, 3, 2]] # 1-P2/4
- [-1, 3, C2f, [128, True]]
- [-1, 1, DynamicConv, [256, 3, 2]] # 3-P3/8
- [-1, 6, C2f, [256, True]]
- [-1, 1, DynamicConv, [512, 3, 2]] # 5-P4/16
- [-1, 6, C2f, [512, True]]
- [-1, 1, DynamicConv, [1024, 3, 2]] # 7-P5/32
- [-1, 3, C2f, [1024, True]]
- [-1, 1, SPPF, [1024, 5]] # 9
# YOLOv8.0n head
head:
- [-1, 1, nn.Upsample, [None, 2, "nearest"]]
- [[-1, 6], 1, Concat, [1]] # cat backbone P4
- [-1, 3, C2f, [512]] # 12
- [-1, 1, nn.Upsample, [None, 2, "nearest"]]
- [[-1, 4], 1, Concat, [1]] # cat backbone P3
- [-1, 3, C2f, [256]] # 15 (P3/8-small)
- [-1, 1, DynamicConv, [256, 3, 2]]
- [[-1, 12], 1, Concat, [1]] # cat head P4
- [-1, 3, C2f, [512]] # 18 (P4/16-medium)
- [-1, 1, DynamicConv, [512, 3, 2]]
- [[-1, 9], 1, Concat, [1]] # cat head P5
- [-1, 3, C2f, [1024]] # 21 (P5/32-large)
- [[15, 18, 21], 1, Detect, [nc]] # Detect(P3, P4, P5)
2.4 yolov8_DynamicBnAct.yaml
# Ultralytics YOLO 🚀, AGPL-3.0 license
# YOLOv8 object detection model with P3-P5 outputs. For Usage examples see https://docs.ultralytics.com/tasks/detect
# Parameters
nc: 80 # number of classes
scales: # model compound scaling constants, i.e. 'model=yolov8n.yaml' will call yolov8.yaml with scale 'n'
# [depth, width, max_channels]
n: [0.33, 0.25, 1024] # YOLOv8n summary: 225 layers, 3157200 parameters, 3157184 gradients, 8.9 GFLOPs
s: [0.33, 0.50, 1024] # YOLOv8s summary: 225 layers, 11166560 parameters, 11166544 gradients, 28.8 GFLOPs
m: [0.67, 0.75, 768] # YOLOv8m summary: 295 layers, 25902640 parameters, 25902624 gradients, 79.3 GFLOPs
l: [1.00, 1.00, 512] # YOLOv8l summary: 365 layers, 43691520 parameters, 43691504 gradients, 165.7 GFLOPs
x: [1.00, 1.25, 512] # YOLOv8x summary: 365 layers, 68229648 parameters, 68229632 gradients, 258.5 GFLOPs
# YOLOv8.0n backbone
backbone:
# [from, repeats, module, args]
- [-1, 1, Conv, [64, 3, 2]] # 0-P1/2
- [-1, 1, Conv, [128, 3, 2]] # 1-P2/4
- [-1, 3, C2f, [128, True]]
- [-1, 1, DynamicBnAct, [256, 3, 2]] # 3-P3/8
- [-1, 6, C2f, [256, True]]
- [-1, 1, DynamicBnAct, [512, 3, 2]] # 5-P4/16
- [-1, 6, C2f, [512, True]]
- [-1, 1, DynamicBnAct, [1024, 3, 2]] # 7-P5/32
- [-1, 3, C2f, [1024, True]]
- [-1, 1, SPPF, [1024, 5]] # 9
# YOLOv8.0n head
head:
- [-1, 1, nn.Upsample, [None, 2, "nearest"]]
- [[-1, 6], 1, Concat, [1]] # cat backbone P4
- [-1, 3, C2f, [512]] # 12
- [-1, 1, nn.Upsample, [None, 2, "nearest"]]
- [[-1, 4], 1, Concat, [1]] # cat backbone P3
- [-1, 3, C2f, [256]] # 15 (P3/8-small)
- [-1, 1, DynamicBnAct, [256, 3, 2]]
- [[-1, 12], 1, Concat, [1]] # cat head P4
- [-1, 3, C2f, [512]] # 18 (P4/16-medium)
- [-1, 1, DynamicBnAct, [512, 3, 2]]
- [[-1, 9], 1, Concat, [1]] # cat head P5
- [-1, 3, C2f, [1024]] # 21 (P5/32-large)
- [[15, 18, 21], 1, Detect, [nc]] # Detect(P3, P4, P5)